Difference between revisions of "Offshore exploration and exploitation"
Sofia Natali (talk | contribs) (Created page with "The offshore is the searching of hydrocarbons resources out of continental platform ambient. The exploration and exploitation are really complex, basically because of his ubic...") |
Sofia Natali (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
==Exploration Instance== | ==Exploration Instance== | ||
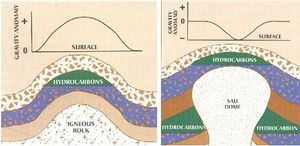
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:Figura 1.jpeg|300px|thumbnail|right|Figure 1: Gravimetric survey]] |
At first, consist in the indirect searching of the resources using geophysics methods: Magnetic survey or register, gravimetric survey and seismic survey. | At first, consist in the indirect searching of the resources using geophysics methods: Magnetic survey or register, gravimetric survey and seismic survey. | ||
Revision as of 02:08, 24 June 2015
The offshore is the searching of hydrocarbons resources out of continental platform ambient. The exploration and exploitation are really complex, basically because of his ubication and the difficulty for the transport of the necessary machineries. As a first step, is necessary make an indirect exploration instance, who in the case of been successful, it goes to a direct exploration instance, that in case of been successful again, it ends finally in an exploitation instance.
Exploration Instance
At first, consist in the indirect searching of the resources using geophysics methods: Magnetic survey or register, gravimetric survey and seismic survey.
- Magnetic survey or register: Consist in the register of the magnetic fields of the rocks, having the Earth magnetic field as reference. These fields are register by a magnetometer installed in a plane that flies over the interest zone. The sedimentaries formation that presents hydrocarbons doesn’t manifests magnetics properties.
- Gravimetric survey: Registers the variation of the rocks density, taking as reference the Earth gravitational field (Figure 1).
- Seismic survey: Is the most used and complete method of all. Register the reflection and refraction variation of induced waves into the surface, where the different formations will act in opposite ways, according their characteristics. These waves are captured in surface or, in the offshore exploration, in a ship, by seismographers, who gaugethe transit time and the intensity of the reflected waves for the subgrade rocks. The method objective is that we be allowed to know how the geology in the prospected area is.
- There are three kinds of seismic models, one more complete and detail than the other one: 2D, 3D and 4D Seismic.
- 2D Seismic: In two dimensions (Figure 2). The sources and receptors of the induced waves are ubicated in a line, having as result a seismic line that cover the structure that we wish to know. The separation of these lines areuicated according to the objective and detail level.
- File:Figure 3Figure 3: 3D Seismic
- 3D Seismic: In three dimensions (Figure 3). For his register the sources and receptors ubicates across perpendicular lines each in the interest area, having as result a seismic data volume, with bigger density respect 2D seismic, and provide better ubication of the structures. This method generates seismic cubes according to the deep, the length of the seismic line and the hydrophones arrangement wide.
- 4D Seismic: Consist in the repetition of a 3D seismic survey in exactly the same original area, after a determinated time. In consequence, the time function is added to a 3d cube.
- Once that the seismic shows successful results, is necessary bring anocean bed survey for knowing his topography, in an area of 30 km2, having as objective establish the substrate conditions for the anchorage or support of the perforation unit. This is realized by bathymetry and cursory seismic. Also it’s has to make a wind, currents and waves study.
Exploitation Instance
After a successful result in the exploration instance, it must to proceed to the offshore platforms installation. These platforms consists in large dimensions structures, that besides extract oil and gas, are used like home for the workers and communication towers. Depending the circumstances, the platform can be fixed at the seafloor, float or be an artificial island. There different kinds of platforms (Figure 4), each one with different especial characteristic according to the deposit and ocean bed kind.