Difference between revisions of "Dip-sealing fault"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
(Initial import) |
(→See also: deleting) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==See also== | ==See also== | ||
* [[Fault seal behavior]] | * [[Fault seal behavior]] | ||
| − | |||
* [[Cross-leaking faults]] | * [[Cross-leaking faults]] | ||
* [[Cross-sealing faults]] | * [[Cross-sealing faults]] | ||
Revision as of 13:58, 31 January 2014
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps |
| Chapter | Evaluating top and fault seal |
| Author | Grant M. Skerlec |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
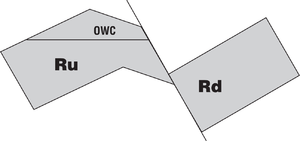
A dip-sealing fault traps hydrocarbons against the fault plane.
Importance of dip-sealing faults
Dip-sealing faults are important because they can create purely fault-dependent traps. No independent structural closure is required for entrapment. Where independent structural closure does exist, as in the figure below, a dip-sealing fault can trap additional volumes of oil against the fault. Dip-sealing faults can trap hundreds of meters of oil without independent closure. In the following figure, both oil and gas are trapped against the fault and have not leaked up the fault zone.
See also
- Fault seal behavior
- Cross-leaking faults
- Cross-sealing faults
- Dip-leaking faults
- Controls on percent fill