Search results
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
- ...ource and reservoir, and geological estimation of the nearest rock unit of source quality. ...chemically]] to determine the [[Maturation|maturity]] of the [[Source rock|source]] from which it was derived. Using this information and an estimate of the3 KB (413 words) - 15:19, 14 February 2022
- | chapter = Evaluating source rocks ...dioxide released is measured. The most widely used pyrolysis technique is Rock-Eval.4 KB (573 words) - 18:22, 8 February 2022
- | chapter = Evaluating source rocks ...on dioxide produced. The LECO method has almost totally been replaced by [[Rock-Eval pyrolysis]]. However, data may still be available from prior analysis.2 KB (354 words) - 15:49, 9 February 2022
- ...clude [[source rock]], [[reservoir rock]], [[seal rock]], and [[overburden rock]]. Relevant processes include trap formation and the generation, expulsion, ...f systems, there may be hybrid systems in which gas-prone and liquid-prone source rocks have contributed to the development of a BCGA.4 KB (469 words) - 19:01, 14 March 2016
File:H4CH12FG8.JPG ...ed amount of hydrocarbon is generated, and at a high heat flow, the source rock is depleted before the trap forms. From Identifying and quantifying signifi(600 × 372 (49 KB)) - 20:32, 13 July 2015- #* Identify the source using petroleum-source rock correlations. #* Locate the general area of the pod of active source rock responsible for the genetically related petroleum occurrences.2 KB (298 words) - 18:35, 25 January 2022
- ...ration|Migration]] to the surface, either from a [[reservoir]] or [[source rock]]. Also called dismigration.440 bytes (58 words) - 21:47, 25 June 2015
- ...[[migration]] path. Only part of the oil and gas generated by the [[source rock]] is actually expelled; of the amount that is expelled, only a small amount ...encies for oil and gas can be as high as 70-80% for very rich, effective [[source rocks]] near preferential [[migration pathways]].4 KB (569 words) - 21:54, 14 February 2022
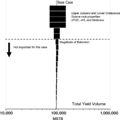
File:H4CH12FG7.JPG ...e most effect on the total oil yield. oTOC and oHI are the original source rock total organic carbon and hydrogen index, respectively. oTOC = original tota(600 × 599 (51 KB)) - 21:12, 9 July 2015- ...anddow_1994>Magoon, L. B., and W. G. Dow, 1994, The petroleum system: From source to trap: [http://archives.datapages.com/data/alt-browse/aapg-special-volume A petroleum system encompasses a pod of active [[source rock]] and all genetically related oil and gas accumulations. It includes all th5 KB (634 words) - 17:54, 25 January 2022
- | chapter = Evaluating source rocks ...roperties|pore fluid chemistry]] can affect the thermal history and thus a rock's rate of maturation.3 KB (421 words) - 18:26, 9 February 2022
- | chapter = Evaluating source rocks ...orded during pyrolysis is T<sub>max</sub>, given in °C. [[:file:evaluating-source-rocks_fig6-6.png|Figure 1]] shows output from a pyrolysis analysis and when3 KB (411 words) - 21:19, 9 February 2022
- ...), each having a specific geographic distribution related to mature source-rock location and [[migration]] paths. We will focus on the High Island-East Bre ==Source table==5 KB (633 words) - 20:02, 18 February 2022
- ! Source rock factors || Migration factors # Calculate the volume of hydrocarbons generated by the [[source rock]], using the formula <math>\text{V} = \text{A} \times \text{T} \times \text6 KB (834 words) - 20:41, 14 February 2022
- ...correlative features, that is, features that result from original [[source rock]] input and not from secondary processes such as [[maturation]], [[migratio [[Category:Oil–oil and oil–source rock correlations]][[Category:Geochemistry]]964 bytes (130 words) - 16:32, 24 June 2015
- | title = Source and Migration Processes and Evaluation Techniques | chapter = Petroleum Source Rocks and Organic Facies2 KB (296 words) - 17:35, 13 April 2022
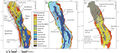
File:M114CH03FG05.jpg ...he (A) main carrier horizon, lowermost Fatehgarh Formation (B) main source rock unit, the Sarovar Member of the Barmer Hill Formation, and (C) Giral Member(700 × 307 (64 KB)) - 17:50, 4 January 2019- | chapter = Evaluating source rocks ...tion of potential source rocks by wireline logs], in Merrill, R., K., ed., Source and Migration Processes and Evaluation Techniques: [http://store.aapg.org/d5 KB (768 words) - 15:48, 9 February 2022
- | chapter = Evaluating source rocks ...top of the oil window. However, this generality applies only if a [[source rock]] is composed of pure type II organic matter (marine kerogen).2 KB (220 words) - 16:10, 10 February 2022
- | chapter = Oil–oil and oil–source rock correlations ...ay]] of the North Sea also yield moderately high-sulfur oils, most clastic source rocks yield oils with less than 0.5% sulfur by weight. However, sulfur cont4 KB (571 words) - 17:34, 15 February 2022