Search results
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Page title matches
- ...ydrocarbon masses, slug flow, cosolution, and compositional changes due to phase changes. Slug flow (or bulk phase flow) is generally accepted as the dominant mechanism of primary [[hydrocar8 KB (1,155 words) - 15:17, 14 February 2022
- #REDIRECT [[Sea level cycle phase and systems tracts]]54 bytes (8 words) - 14:52, 21 November 2014
- ...el changes are correlated to the early phase of lowstand fall and the late phase of low-stand to transgressive rise, respectively. ...entary-basin-analysis_fig4-18.png|Figure 3]]). Within the initial lowering phase, the rate of slope and intraslope basin sediment accumulation increases, wi11 KB (1,548 words) - 16:58, 24 February 2022
- ..., 1987, Theoretical aspects of cap-rock and fault seals for single and two-phase hydrocarbon columns: Marine and Petroleum Geology, vol. 4, no. 4, p. 274– ==Single phase vs. two phase==3 KB (445 words) - 20:56, 31 March 2022
- ...on discusses the concept of sea level cycle phase, identification of cycle phase, construction of a cycle chart, and how sea level cycles of different durat ...ion methodology of [[sequence stratigraphy]] helps us recognize each cycle phase and provides a nomenclature to describe each element.<ref name=ch04r99>Vail8 KB (1,103 words) - 21:21, 23 February 2022
- ..., 1987, Theoretical aspects of cap-rock and fault seals for single and two-phase hydrocarbon columns: Marine and Petroleum Geology, vol. 4, no. 4, p. 274– * [[Seal capacity and two-phase hydrocarbon columns]]5 KB (765 words) - 20:55, 31 March 2022
- #REDIRECT [[Seal capacity variation with depth and hydrocarbon phase]]70 bytes (9 words) - 15:15, 21 July 2014
Page text matches
- ..., 1987, Theoretical aspects of cap-rock and fault seals for single and two-phase hydrocarbon columns: Marine and Petroleum Geology, vol. 4, no. 4, p. 274– ==Single phase vs. two phase==3 KB (445 words) - 20:56, 31 March 2022
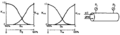
File:Fundamentals-of-fluid-flow fig3.png Two-phase relative permeability.(887 × 260 (6 KB)) - 01:52, 14 January 2014- #REDIRECT [[Seal capacity variation with depth and hydrocarbon phase]]70 bytes (9 words) - 15:15, 21 July 2014
- #REDIRECT [[Sea level cycle phase and systems tracts]]54 bytes (8 words) - 14:52, 21 November 2014
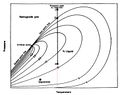
File:AlAhmadiTawfiqFigure1.jpg Phase envelope of retrograde gas condensate (Parvizi, 2010).(1,452 × 1,150 (168 KB)) - 22:49, 9 November 2021
File:Petroleum-reservoir-fluid-properties fig2.png Pressure-temperature phase diagrams of gas cap and oil fluids in a reservoir that is Initially at satu(952 × 853 (12 KB)) - 01:52, 14 January 2014- ...ious rock types. In addition, a number of other factors—depth, hydrocarbon phase, seal thickness, fault-dependent leak points—affect the height of trapped * [[Seal capacity variation with depth and hydrocarbon phase]]1 KB (179 words) - 20:54, 31 March 2022
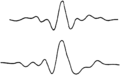
File:Vertical-and-lateral-seismic-resolution-and-attenuation fig2.png A 1.5-octave zero-phase wavelet passing frequencies between 14 and 65 Hz that passes 100% between 2(908 × 571 (13 KB)) - 19:35, 14 January 2014
File:Petroleum-reservoir-fluid-properties fig1.png Pressure-temperature phase diagram. Reservoir classification would be <italic>oil</italic> if reservoi(932 × 924 (22 KB)) - 01:52, 14 January 2014- Subdivision of each [[Sea level cycle phase and systems tracts|sea level cycle]] into its depositional phases helps us * [[Sea level cycle phase]]2 KB (215 words) - 15:43, 23 February 2022
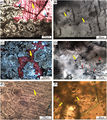
File:BLTN12220fig5.jpg ...by gas reacting with anhydrite, well D4, 4793.00 m (15,721.04 ft). (F) Two-phase aqueous fluid inclusions (yellow arrows) commonly present in calcite. Note(444 × 500 (324 KB)) - 13:22, 13 August 2014- ...c data]] [[attributes]], reflection strength, coherence, and instantaneous phase. These attributes are well suited to stratigraphic interpretation and are a | Instantaneous phase4 KB (481 words) - 18:20, 4 February 2022
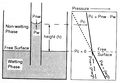
File:Charles-l-vavra-john-g-kaldi-robert-m-sneider capillary-pressure 2.jpg The wetting phase rises above the original or free surface in the capillary tube experiment u(1,200 × 828 (279 KB)) - 17:41, 13 September 2013- ===Acquisition phase=== The acquisition phase involves the following functions:5 KB (759 words) - 19:25, 19 January 2022

File:Capillary-pressure fig2.png The wetting phase rises above the original or free surface in the capillary tube experiment u(947 × 675 (25 KB)) - 18:22, 14 January 2014
File:Charles-l-vavra-john-g-kaldi-robert-m-sneider capillary-pressure 1.jpg ...wettability is the contact angle (θ), which is measured through the denser phase.(1,200 × 434 (272 KB)) - 17:41, 13 September 2013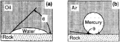
File:Capillary-pressure fig1.png ...wettability is the contact angle (6), which is measured through the denser phase.(941 × 333 (26 KB)) - 18:22, 14 January 2014- ...ydrocarbon masses, slug flow, cosolution, and compositional changes due to phase changes. Slug flow (or bulk phase flow) is generally accepted as the dominant mechanism of primary [[hydrocar8 KB (1,155 words) - 15:17, 14 February 2022
- ...a time series of [[cross section]]s, showing the geologic elements of each phase. Because all basins are three dimensional, care must be taken to assemble e file:sedimentary-basin-analysis_fig4-9.png|{{figure number|3}}Phase E began during the mid-Cenomanian with a rapid fall and rise of sea level s7 KB (1,044 words) - 16:34, 22 February 2022
- # Identify the stratigraphic interval of a single depositional phase that has potential for containing reservoir rocks, i.e., [[Third-order sequ ...]], parallel reflections, chaotic reflections within a single depositional phase).4 KB (491 words) - 14:27, 21 March 2022