Spontaneous potential logs in water resistivity calculation
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps |
| Chapter | Predicting reservoir system quality and performance |
| Author | Dan J. Hartmann, Edward A. Beaumont |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
Water resistivity or Rw, is a critical component of log analysis in calculating water saturation using the Archie equation. Rw can be measured from a sample of formation water taken from the zone of interest at the well site or a nearby well, or it can be calculated using spontaneous potential (SP) log data.
Data required[edit]
To calculate Rw from SP, we need the following data:
- Resistivity of the mud filtrate (Rmf) at measured temperature, found on the log header. If only mud resistivity (Rm) is given, convert it to Rmf as explained below.
- Bottom-hole temperature (BHT) and total depth, found on the log header.
- SP reading from a porous zone at least length::20 ft thick. (A bed thickness correction is necessary if the zone SP is measured from is less than length::20 ft thick.)
Converting rm to rmf[edit]
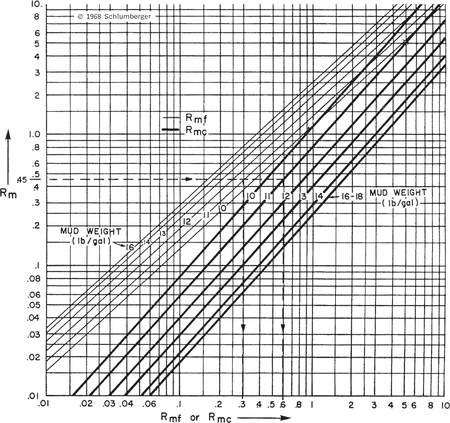
If the log header gives Rm only, then Rm must be converted to Rmf using this procedure:
- Enter Rm and move across (Figure 1) to the appropriate mud weight.
- Project to the bottom of the chart to estimate Rmf
Steps for calculating rw[edit]
There are five steps for calculating Rw from the SP log. The list below summarizes these steps, which are detailed in the rest of this section.
- Estimate formation temperature.
- Convert Rmf to formation temperature.
- Convert Rmf to Rmfeq .
- Read SP response and estimate Rwe .
- Convert Rwe to Rw and NaCl at formation temperature.
Step 1: Estimate formation temperature[edit]
Formation temperature (Tf) can be estimated by using the following formula:
where:
- Ts = average surface temperature
- Df = depth to the formation
- BHT = bottom-hole temperature (found on log header)
- TD = total depth (make sure BHT and TD are from same log run)
Step 2: convert rmf to rmf at formation temperature[edit]
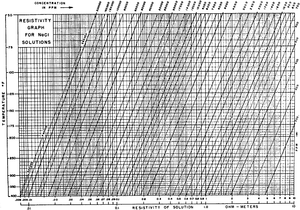
Follow this procedure to convert Rmf (measured at surface temperature) to Rmf at formation temperature.
- Enter Figure 2 along the resistivity of solution axis and the temperature axis using the measured values for Rmf and surface temperature found on the log header.
- Follow the appropriate salinity line intercepted at step 1 to the appropriate formation temperature and mark on the chart.
- Project down the chart from this mark to the resistivity scale and read Rmf at formation temperature. Record the value of Rmf at a specific temperature.
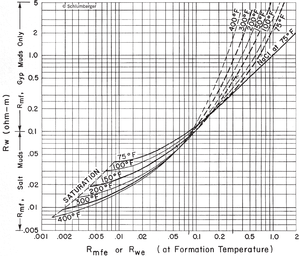
Step 3: convert rmf to rmf eq[edit]
Use the Rmf at formation temperature obtained above and follow the procedure below to convert Rmf to equivalent mud filtrate resistivity (Rmf eq).
- Enter Figure 3 with Rmf at formation temperature on the vertical axis.
- Move across the chart to the appropriate formation temperature contour, and mark this point on the figure.
- Read down to Rmfeq . This value is used in the equation Rwe = Rmfeq (Rmfeq /Rwe value).
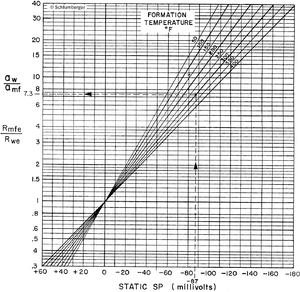
Step 4: convert SP to rwe[edit]
Follow the procedure below to convert SP from the zone of interest to equivalent formation water resistivity (Rwe).
- On the log, establish the shale base line for the SP curve.
- Read the maximum SP response in a zone at least length::20 ft thick.
- Enter the base of Figure 4 with SP (SP is negative if it deflects to the left of the shale base line). Follow the SP grid line up the chart to the appropriate formation temperature. At this point, move across the chart and read the Rmf eq /Rwe Value.
- Solve for Rwe using the equation Rwe = Rmfeq /(Rmfeq /Rwe value).
Step 5: convert rwe to rw[edit]
Follow the procedure below to convert Rwe to Rw.
- Enter Figure 3 again with Rwe (along the base). Move up the chart until Rwe intersects the temperature slope.
- Directly across from the intersection point, read Rw from the vertical axis.