Fracking
| Wiki Write-Off Entry | |
|---|---|

| |
| Student Chapter | Universitas Diponegoro |
| Competition | June 2015 |
Fracking is an attempt to increase the productivity of the formation by injecting a fluid, combine of water, chemical and wedge fractures (proppant) into the wellbore. Fracking is used in formations with low permeability such as tight gas, shale gas, tight oil and gas coal seam.
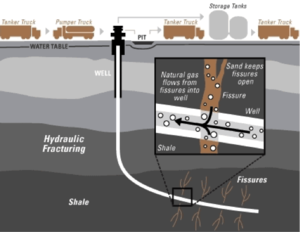
How to do fracking
Fracking technique begins by drilling vertically up to the target reservoir layer. Drilling is then followed by the installation of a protective casing or drilling gas flow so as not to contaminate the soil environment leaking around the well. Then, the cracking (fissures) or destruction of the devices in the area perforated horizontal well at some point. The next stage is the injection of water, sand and chemicals (fracking fluid) high pressure into the well. Injection, followed by withdrawal or pumping back the fracking fluid to the surface. Fracking fluid is lifted to the surface of the back is often called produced water or flowback water. In practice, the withdrawal of fracking fluid to the surface only managed to restore 25% to 50% of the volume injected so that it can be concluded that the rest of the fracking fluid that can not be recovered still inside the shale. After the withdrawal of fracking fluid, and gas in the shale can be economically recovered. As mentioned earlier, during the productive gas wells produce, usually hydraulic fracturing is done up to 18 times.
Fracking impact
- Positive Impact of Fracking
- Increase the productivity development of gas up to 70%
- Negative impact of Fracking
- Pollution of water near the surface of the soil used in areas Area residents drilling field
- Place the water availability slightly, resulting in the use of fracking become unbelievably expensive and sometimes uneconomical.
- mengkibatkan demage formation and can reduce long-term production.
- Chemical which digunaakan for injection containing BTEX (benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes), which is a cause of cancer
Prevention
Waste of hydraulic fracturing done in 2 ways, namely:
- Infiltration Impoundment, which is naturally evaporating or evaporation. Evaporating process is carried out by mixing the aerosol into an already filled water dewatering results. The process is carried out at least 2 times until water is considered feasible to naturally evaporated or removed kesaluran common disposal.
- Saved for reuse at a later date.
References
Other resources
- Al-Jubori, A., and S. Johnston, 2009, Coalbed Methane: Clean Energy for the World, in Characteristics of Coalbed Methane Production and Associated Hydraulic Fracturing Practices
- Fatahillah, M. R., 2011, Efek Teknik Hydraulic Fracturing dalam Eksplorasi Shale Gas di Amerika Serikat
- Hal Macartney, 2011, EPA Hydraulic Fracturing Workshop: Hydraulic Fracturing, in Coalbed Methane Development Raton Basin, Southern Colorado
- http://issuu.com/petromagz/docs/petromagz_november_2013
- iesc.environment.gov.au/reserch/chemicals
- lockthegate.org.au/about_coal_seam_gas