Sandstone provenance and characterization
| Wiki Write-Off Entry | |
|---|---|

| |
| Student Chapter | Universitas Diponegoro |
| Competition | June 2015 |
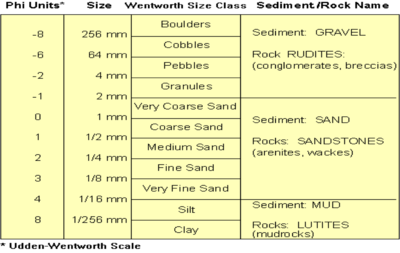
Sandstone is one of sedimentary rocks which have a large distribution in whole a part of the earth. Between 20% until 25% is the rate of sandstone distribution in each earth layer. From the heights until the deep ocean, we still found the sandstone layers in each portion. Sedimentary rock is rock that formed by diagenesis of other rock that has been sedimented. The sandstone composed of sediment materials from others process such as weathering and erosion of any other rocks. The reworking process is being continuously to provide the sediment materials which transported until each sedimentary basin. The rough materials will proceed to be smaller and smoother materials depend on how far it transported. The sandstone is meaning sedimentary rocks which have the size rate between 1/16 until 2 mm. The size that is called sand can be very rough until the smallest one is very fine. Sandstone have the moderate grain size, not too rough like pebble, granule, cobble or boulder but not too fine like silt or clay. So, there is easier to form the sand grain size, to transport them and to make them deposited. That’s why we can found the sand deposit or sandstone almost in everywhere.
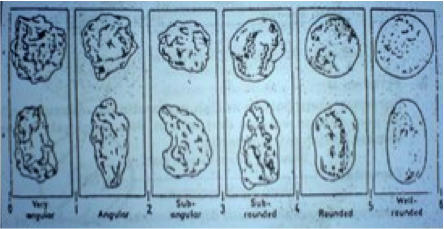
We can intepreted the clastic by its texture. Texture is the appearance related to the size and shape of the grain as well as its composition.[1] Granules composed and bound by cement and persistence of the cavity between the nut. Dokontrol formation by the media and means of transportation (Jackson, 1970; Reineck and Singh, 1975). Discussion textures include: grain size, sorting, roundness, shape, porocity, fabric
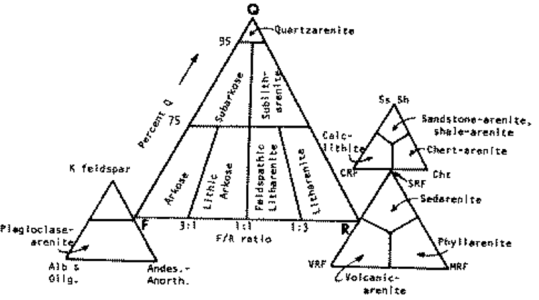
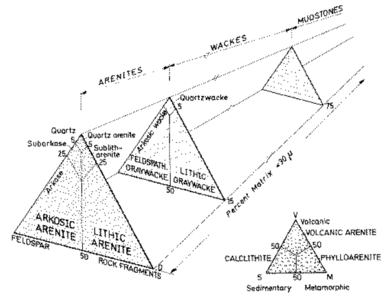
The sandstone itself was classified by two person. Folk in 1980, and Dott in1964 These are the classification of sandstone.
We can know more about sandstone by its composition, in Folk and Dott Clasification, we have to know about quartz, feldspar, and rock fragments that compose the sandstone. When we figure it out, we can named it by looking the classification.
The difference about sedimentary rock are clastic and non-clastic. The clastic sedimentary is the formation of precipitation or planning denritus rock back there. Origin rocks can be igneous, and metamorphic rocks sedimnen. In the formation of clastic sedimentary rocks have experienced diagnesa ie changes that took place at low temperatures in a sediment during and after lithification. Composed by clastics that happens because the deposition process mechanically and encountered allogenic minerals. Allogenic minerals are minerals that are not formed on the environment during sedimentation or sedimentation occurs. These minerals come from rocks that have undergone transport origin and then deposited on the environment sedimentation.
There are many properties of sandstone such as the external structure because of tectonic, or sedimentary structure because of depositional process and kinds of many factors that influence the deposit. The sedimentary structure can help us to understand how the condition when the sand materials deposited such as current’s power, and burial deformation. The other one properties that was important is the composition of the sandstone. Knowing the composition, may help us to understand where is the sand sediment come from and what is the source rocks of deposit, so we can interpret the sedimentation history of each kind of sandstone. The study of this case is sandstone provenance.
Definition of provenance
Provenance is the source rocks before reworking process, sandstone can composed by igneous rock, metamorphic rock or other sedimentary rock fragment. That’s why important to know where is the sandstone came from, because transportation process cannot tell us about it well, but the composition will tell us much more. Based on grain mineralogy, sandstones are divided into three groups: Quartz arenite, feldspathic arenite, dan lithic arenite.
Quartz arenite provenance
Quartz arenite is sandstone which has a granular silica composition more than 90 percent of which consists of quartz, chert, and quartzose rock fragments. In general, its color is light gray. But, it can occur with a pink, yellow, or brown color due to iron oxide. This sandstone usually lithified and cemented by silica and carbonate cement. Usually associated with cratonic, aeolian, beaches and continental shelf environment. Usually deposited shallow marine carbonate interlayered with feldspar and sandstones. In general have a maturity ranging from mature to supermature. Quartz wacke rarely formed. Usually forming sedimentary structures like cross-bedding, and quite often also formed ripple marks. Fossils are rare because usually deposited in an environment that very difficult to preserve fossils like the eolian environments. Pettijohn (1963) says that this type of sandstone make up one third of the total sandstones. Quartz arenite can be formed from the deposition of the first cycle of crystalline igneous or metamorphic rocks, and repeated destruction of quartz grains in sedimentary rocks.
Feldsphatic arenite provenance
Feldspathic arenite containing less than 90 percent of the composition of quartz. Feldspar is the main composition. Feldspathic arenite may contain fragments of unstable rock, and a little amount of other minerals such as mica and heavy minerals. Some feldspathic arenite have pink or red color because of the presence of potassium feldspar or iron oxide. There are also colored light gray to white. These sandstones are usually medium to coarse grained and can contain a high percentage of granules with angular until subangular roundness. The content of the matrix can appear as the rest up to more than 15 percent, and sorting of grains can present as moderate to poorly sorted. Feldspathic sandstones are generally immature in textural maturity. Feldspathic arenite can not be judged from the structure of the sediment. Bedding can emerge from the laminate parallel to the crossbed. Fossils may appear in the layer deposited on the sea. Feldspathic arenites usually appear on the craton or the continental shelf, which can be associated with conglomerate, quartz lithic arenite, carbonate rock, or evaporites. This sandstone may also appear on the succession of sedimentary basins deposited on an unstable or deep sea, and moving arc setting. According to Pettijohn (1963) Arkose make up about 15 percent of all sandstones. Some Arkose formed in situ when the granite and related rocks disintegrate and generate granular sediments. Most of the material feldspathic sandstones derived from primary crystalline granitic rocks, such as granite or metasomatic rocks containing abundant potassium feldspar. Mineral contained in sandstones is mostly a form of plagioclase feldspar derived from quartz diorite or volcanic rock. Feldspar contained on this sandstone comes from arid to cool climates when the chemical weathering process is reduced.
Lithic arenite provenance
Lithic arenite consists of a fairly high content of unstable rock fragments such as volcanic rocks and metamorphic rocks clastics. Lithic arenite fragments can be composed of chert. These sandstones may contain less than 90 percent of quartz grain and assemblage of rock fragments are more unstable than feldspar. The color is usually light gray and dark gray. Most lithic arenite are poorly sorted. Most of lithic arenite have an immature to submature textural maturity. Lithic arenite may appear on marine turbidite sediments and fluvial. Pettijohn (1963) estimates that the lithic arenite and graywacke make up nearly half of the sandstones. The lithic fragments indicates the source of sediments derived from high relief environment. These sandstones are usually present on the alluvial fan but can also be present in the fold thrust belt in the Foreland basin. Volcaniclastic sandstone is a special kind of lithic arenite derived from volcanic detritus. Usually formed of pyroclastic material that transported or reworked. Typically characterized by the presence of euhedral feldspar, pumice fragments, glass shards, fragments of volcanic rocks, and little quartz content.
Other types of sandstones provenance
Other types of sandstones that are not included in the above categories are formed by the biochemical and chemical processes. It is also called the sandstone rock hybrid varieties that have the form of glauconitic sandstones, phospate sandstones, and calcarenaceous sandstones. The rock is actually not the original sandstone.
All of these properties can explain the variety of sandstone based on every composition contained. In the nature, rocks has made, are making, and will make by the process that will not stop by anything. The rock cycle become the reason why the earth always evolved time by time to produce other rocks and geomorphology. Understanding the characteristics of sandstone or other rocks, will help us understand about the evolution of the earth such as sedimentation, up and down of sea level, tectonic, volcanism, and also transformation of sedimentary environment. Because present is the key to the past and also to the future.
References
- ↑ Pettijohn, F. J., 1975, Sedimentary Rock, 3rd ed.: Harper Row, New York, 628p
- Pettijohn, F.J., P.E. Potter, and R. Siever, 1987, Sand and Sandstone, 2nd ed.: Springer-Verlag,New Nyork,553 p.
- Boggs, Jr., 2006, Principle of Sedimentology and Stratigraphy, 4th ed.: Pearson Education, New York,131p.