Difference between revisions of "Hydrocarbon accumulation: the seven critical elements"
FWhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
Cwhitehurst (talk | contribs) m (added Category:Treatise Handbook 3 using HotCat) |
||
| (10 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| part = Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps | | part = Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps | ||
| chapter = Value of geological fieldwork | | chapter = Value of geological fieldwork | ||
| − | | frompg = 19- | + | | frompg = 19-11 |
| − | | topg = 19- | + | | topg = 19-12 |
| author = Denise M. Stone | | author = Denise M. Stone | ||
| link = http://archives.datapages.com/data/specpubs/beaumont/ch19/ch19.htm | | link = http://archives.datapages.com/data/specpubs/beaumont/ch19/ch19.htm | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Seven critical elements are necessary for subsurface [[hydrocarbon]] [[accumulation]]s to occur: | Seven critical elements are necessary for subsurface [[hydrocarbon]] [[accumulation]]s to occur: | ||
| − | * Reservoir rock | + | * [[Reservoir]] rock |
| − | * Source rock | + | * [[Source rock]] |
| − | * Seal | + | * [[Seal]] |
* Thermal history | * Thermal history | ||
| − | * Migration and | + | * [[Migration]] and [[trap]]ping of [[hydrocarbon]]s |
* Geologic history of the basin | * Geologic history of the basin | ||
* Structural history and style | * Structural history and style | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
Exploration risk is best understood by studying historically what has and has not been successful in a basin. In other words, what combination of the seven critical elements occurred to form existing fields and, conversely, what are the main reasons for the [[dry hole]]s in that same basin? Is a common element responsible for the dry holes? | Exploration risk is best understood by studying historically what has and has not been successful in a basin. In other words, what combination of the seven critical elements occurred to form existing fields and, conversely, what are the main reasons for the [[dry hole]]s in that same basin? Is a common element responsible for the dry holes? | ||
| − | The goal of an exploration effort is to use all the data available to identify fully the technical risks and recommend the best course of action and investment. Action following a field project might range from no action, to acquiring more data in key areas, to drilling a well. | + | The goal of an exploration effort is to use all the data available to identify fully the technical risks and recommend the best course of action and investment. Action following a field project might range from no action, to acquiring more data in key areas, to [[drilling a well]]. |
==Critical element checklist== | ==Critical element checklist== | ||
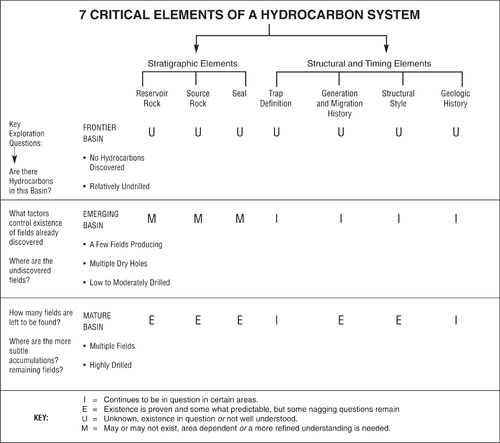
| − | The following checklist summarizes key | + | |
| + | [[file:value-of-geological-fieldwork_fig19-1.png|500px|thumb|{{figure number|1}}A summary of each of the seven critical elements of a hydrocarbon system with respect to the exploration maturity of the basin.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The following checklist summarizes key attributes of the seven critical elements. The working explorer should have a general understanding of these attributes in the basin studied. | ||
===Reservoir rock=== | ===Reservoir rock=== | ||
| Line 37: | Line 40: | ||
* Sedimentary rock type(s) | * Sedimentary rock type(s) | ||
* Gross thickness range | * Gross thickness range | ||
| − | * Lateral continuity (faulted?) | + | * [[Lateral]] continuity (faulted?) |
* Mappability | * Mappability | ||
| − | * Depth of burial | + | * Depth of burial |
| − | * Outcrop occurrences | + | * Structural relief of reservoir top |
| + | * [http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/outcrop Outcrop] occurrences | ||
Character of upper and lower boundaries | Character of upper and lower boundaries | ||
| Line 52: | Line 56: | ||
* Depositional environment | * Depositional environment | ||
| − | * Facies distribution | + | * [[Lithofacies|Facies]] distribution |
| − | * Provenance | + | * [http://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/provenance Provenance] |
* Internal stratigraphic subdivisions | * Internal stratigraphic subdivisions | ||
| − | * Age diagnostic criteria: fossils, intrusives, marker horizons | + | * Age diagnostic criteria: fossils, [http://www.geolsoc.org.uk/ks3/gsl/education/resources/rockcycle/page3598.html intrusives], marker horizons |
* Electric log responses | * Electric log responses | ||
* Pay distribution: vertical, lateral | * Pay distribution: vertical, lateral | ||
| Line 65: | Line 69: | ||
* Texture: [[grain size]], [[Core_description#Maturity|sorting]], roundness, crystallinity | * Texture: [[grain size]], [[Core_description#Maturity|sorting]], roundness, crystallinity | ||
* Degree of cementation | * Degree of cementation | ||
| − | * Diagenetic alteration | + | * [[Diagenesis|Diagenetic]] alteration |
* Microfossils | * Microfossils | ||
* [[Fracture]]s | * [[Fracture]]s | ||
| Line 78: | Line 82: | ||
* Organic richness | * Organic richness | ||
* Thermal maturity | * Thermal maturity | ||
| − | * Kerogen type | + | * [[Kerogen types|Kerogen type]] |
| − | * Depositional environment | + | * [[Depositional environments|Depositional environment]] |
| − | * Facies | + | * [[Lithofacies|Facies]] |
* Mappability | * Mappability | ||
* Carbonate vs. clastic | * Carbonate vs. clastic | ||
| Line 92: | Line 96: | ||
* [[Capillary pressure]] | * [[Capillary pressure]] | ||
* Lateral continuity of sealing formations | * Lateral continuity of sealing formations | ||
| − | * Presence of | + | * Presence of [[evaporite]]s |
| − | * Fracture systems | + | * [[Fracture]] systems |
===Thermal history=== | ===Thermal history=== | ||
| Line 108: | Line 112: | ||
* [[Fracture]]s | * [[Fracture]]s | ||
* Lateral [[permeability]] and [[porosity]] | * Lateral [[permeability]] and [[porosity]] | ||
| − | * Controls on migration | + | * Controls on [[migration]] |
===Geologic history=== | ===Geologic history=== | ||
| − | * Main tectonic events: compressional, tensional, wrench | + | * Main tectonic events: compressional, tensional, [http://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/en/Terms.aspx?LookIn=term%20name&filter=wrench%20fault wrench] |
* Structural overprinting | * Structural overprinting | ||
* Depositional history: continental, marine | * Depositional history: continental, marine | ||
| Line 120: | Line 124: | ||
* Significant episodes of volcanism, subsidence, uplift, erosion | * Significant episodes of volcanism, subsidence, uplift, erosion | ||
* Rates of deposition | * Rates of deposition | ||
| − | * Paleotopography | + | * [[Paleogeography|Paleotopography]] |
| − | * | + | * [[Paleoclimatology|Paleoclimate]] |
| − | + | * [http://www.stratigraphy.org/upload/bak/chron.htm Chronostratigraphy] | |
| − | * Chronostratigraphy | ||
===Structural history and style=== | ===Structural history and style=== | ||
| Line 136: | Line 139: | ||
* Major faults vs. minor faults | * Major faults vs. minor faults | ||
* Zones of weakness | * Zones of weakness | ||
| − | * Dip domains | + | * [[Dip]] domains |
| − | * Outcrop patterns | + | * [http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/outcrop Outcrop] patterns |
| − | * Dip and | + | * Dip and [[strike]] trends |
| − | + | * Average [[Wikipedia:Fault_(geology)#Slip.2C_heave.2C_throw|throw]] on faults | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | * [[ | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
| Line 152: | Line 151: | ||
[[Category:Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps]] | [[Category:Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps]] | ||
[[Category:Value of geological fieldwork]] | [[Category:Value of geological fieldwork]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Treatise Handbook 3]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:47, 1 February 2022
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps |
| Chapter | Value of geological fieldwork |
| Author | Denise M. Stone |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
Seven critical elements are necessary for subsurface hydrocarbon accumulations to occur:
- Reservoir rock
- Source rock
- Seal
- Thermal history
- Migration and trapping of hydrocarbons
- Geologic history of the basin
- Structural history and style
Criticality
Exploration risk is best understood by studying historically what has and has not been successful in a basin. In other words, what combination of the seven critical elements occurred to form existing fields and, conversely, what are the main reasons for the dry holes in that same basin? Is a common element responsible for the dry holes?
The goal of an exploration effort is to use all the data available to identify fully the technical risks and recommend the best course of action and investment. Action following a field project might range from no action, to acquiring more data in key areas, to drilling a well.
Critical element checklist
The following checklist summarizes key attributes of the seven critical elements. The working explorer should have a general understanding of these attributes in the basin studied.
Reservoir rock
General 3-D definition
- Sedimentary rock type(s)
- Gross thickness range
- Lateral continuity (faulted?)
- Mappability
- Depth of burial
- Structural relief of reservoir top
- Outcrop occurrences
Character of upper and lower boundaries
- Origin: erosional vs. depositional
- Nature: abrupt vs. gradational
- Seismic reflectivity
- Conformability
Diagnostic features
- Depositional environment
- Facies distribution
- Provenance
- Internal stratigraphic subdivisions
- Age diagnostic criteria: fossils, intrusives, marker horizons
- Electric log responses
- Pay distribution: vertical, lateral
- Sedimentary structures
Petrographic characteristics
- Composition: framework grain mineralogy, crystallinity
- Texture: grain size, sorting, roundness, crystallinity
- Degree of cementation
- Diagenetic alteration
- Microfossils
- Fractures
- Porosity
- Permeability
Source rock
- Age
- Thickness
- Lateral continuity
- Organic richness
- Thermal maturity
- Kerogen type
- Depositional environment
- Facies
- Mappability
- Carbonate vs. clastic
- Depth of burial
Seal
- Vertical seals
- Lateral seals
- Lithology of potential seals
- Capillary pressure
- Lateral continuity of sealing formations
- Presence of evaporites
- Fracture systems
Thermal history
- Rates of deposition
- Rates of burial
- Paleogeothermal gradient
- Tectonic history
- Location of kitchen areas
Migration and trapping
- Fault juxtaposition
- Fractures
- Lateral permeability and porosity
- Controls on migration
Geologic history
- Main tectonic events: compressional, tensional, wrench
- Structural overprinting
- Depositional history: continental, marine
- Episodes of subsidence: regional, local
- Controls on subsidence
- Unconformities
- Significant episodes of volcanism, subsidence, uplift, erosion
- Rates of deposition
- Paleotopography
- Paleoclimate
- Chronostratigraphy
Structural history and style
- Compressional vs. tensional basin
- Main structural elements
- Tectonic development
- Sequence of events
- Structural overprinting
- Fault trends: major and minor
- Basin boundary faults
- Major faults vs. minor faults
- Zones of weakness
- Dip domains
- Outcrop patterns
- Dip and strike trends
- Average throw on faults