Fluvial input through time: Gulf of Mexico example
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Critical elements of the petroleum system |
| Chapter | Sedimentary basin analysis |
| Author | John M. Armentrout |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
The Late Cretaceous to Holocene depositional history of the northern Gulf of Mexico (GOM) continental margin has been influenced by several factors:[1]
- Fluvial supply system and delta formation
- Subsidence
- Diapiric and tectonic movement
- Fluctuation in sea level
Summary of GOM fluvial history
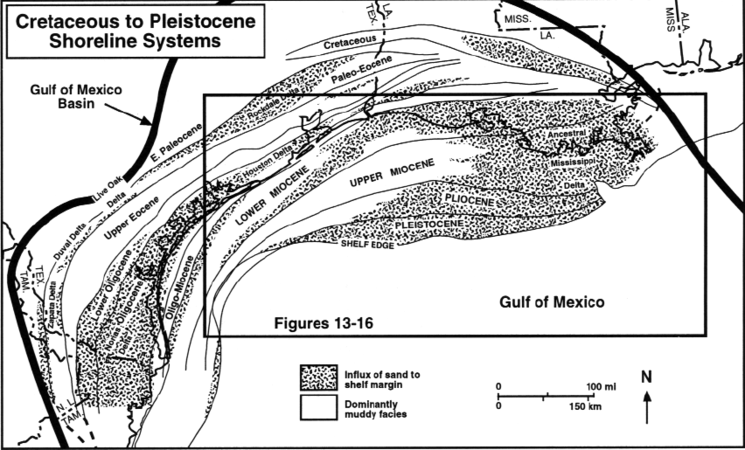
Figure 1 Major sand influxes into the northern Gulf of Mexico from Late Cretaceous to Holocene. After Winker;[2] courtesy Gulf Coast Association of Geological Societies.
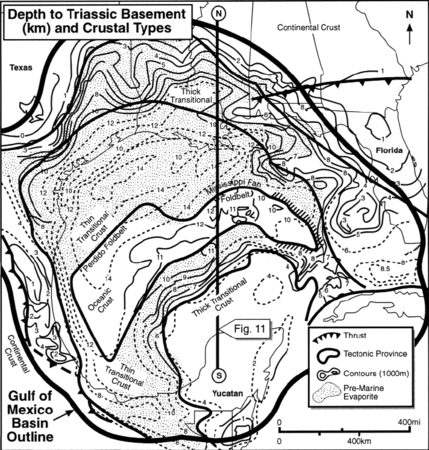
Figure 2 Tectonic map of the GOM basin. Modified from Buffler;[3] courtesy New Orleans Geological Society.
Mesozoic and Cenozoic fluvial systems have filled in the northern margins of the GOM rift basin, prograding the continental margin of one area until sediment input shifts to another area (Figure 1). Subsidence is related to basement cooling or differential response of basement types to loading (Figure 2). Formation of diapirs and tectonic movement of growth-fault systems has already being discussed as it relates to sediment loading. Fluctuation in sea level is discussed in Sea level cycle phase.
See also
References
- ↑ Coleman, J. M., and H. H. Roberts, 1991, Mississippi River depositional system: model for the Gulf Coast Tertiary, in D. Goldthwaite, ed., An Introduction to Central Gulf Coast Geology: New Orleans Geological Society, p. 99–121.
- ↑ Winker, C. D., 1982, Cenozoic shelf margins, northwestern Gulf of Mexico: Gulf Coast Assoc. of Geological Societies Transactions, vol. 32, p. 427-448.
- ↑ Buffler, R. T., 1991, Early evolution of the Gulf of Mexico basin, in D. Goldthwaite, ed., An introduction to central Gulf Coast geology: New Orleans Gulf Coast Geological Society, p. 1-16.