Difference between revisions of "Fold"
Cwhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{{publication | {{publication | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = ST53Cover.jpg |
| width = 120px | | width = 120px | ||
| series = Studies in Geology | | series = Studies in Geology | ||
| Line 16: | Line 14: | ||
| isbn = 0891810609 | | isbn = 0891810609 | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
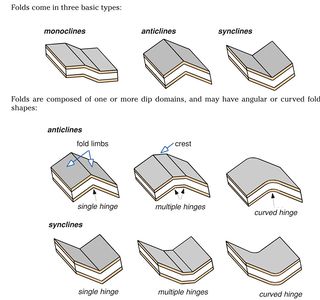
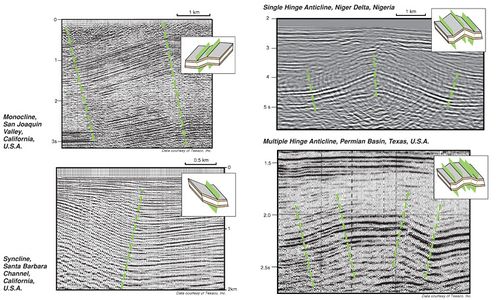
Folds are bends or flexures of layered rock that form in response to motion along [[fault]]s, [[diapirism]], [[compaction]], and regional subsidence or [[uplift]]. Folds are expressed in [[seismic reflection profile]]s as one or more regions of dipping reflections ([[dip]] domains) that correspond to inclined [[stratigraphic]] contacts. | Folds are bends or flexures of layered rock that form in response to motion along [[fault]]s, [[diapirism]], [[compaction]], and regional subsidence or [[uplift]]. Folds are expressed in [[seismic reflection profile]]s as one or more regions of dipping reflections ([[dip]] domains) that correspond to inclined [[stratigraphic]] contacts. | ||
| − | + | <gallery mode=packed heights=200px widths=200px> | |
| + | File:ST53_Part01_Pg03A.jpg|{{figure number|1}} | ||
| + | File:ST53_Part01_Pg03B.jpg|{{figure number|2}} | ||
| + | File:ST53_Part01_Pg04.jpg|{{figure number|3}}Folds in seismic sections. | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
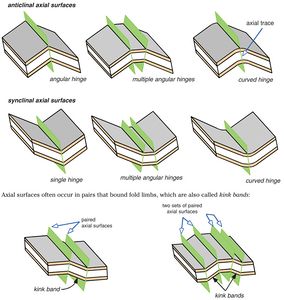
Dip domains are separated by [[axial]] surfaces; imaginary planes which, when viewed in two dimensions, form axial traces. [[Anticlinal]] axial surfaces occupy concave-downward [[fold hinge]]s; [[synclinal]] axial surfaces occupy concave-upward fold hinges. | Dip domains are separated by [[axial]] surfaces; imaginary planes which, when viewed in two dimensions, form axial traces. [[Anticlinal]] axial surfaces occupy concave-downward [[fold hinge]]s; [[synclinal]] axial surfaces occupy concave-upward fold hinges. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Folds and bedding thickness== | ||
| + | Folds are classified based on whether or not the thickness of stratigraphic layers changes in dip domains or across axial surfaces. | ||
| + | |||
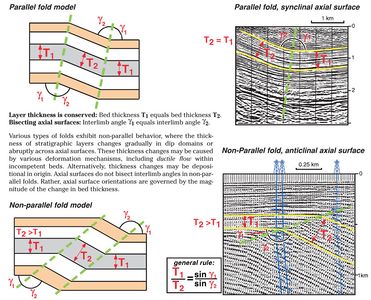
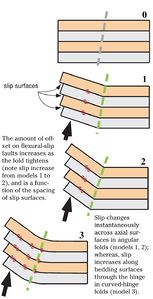
| + | Parallel folds preserve layer thickness, and are common in [[strata]] that deformed predominantly by [[flexural slip]] (see inset at right on [[:file:ST53_Part01_Pg05A.jpg|Figure 4]]). Axial surfaces bisect inter-limb angles in parallel folds. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery mode=packed heights=200px widths=200px> | ||
| + | File:ST53_Part01_Pg05A.jpg|{{figure number|4}} | ||
| + | File:ST53_Part01_Pg05B.jpg|{{figure number|5}} | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Parallel folds commonly form by a [[deformation]] mechanism called flexural slip, where folding is accommodated by motions on minor [[fault]]s that occur along some mechanical layering—usually bedding. Flexural-slip surfaces, which can be observed in [[core]] or [[outcrop]], may vary in spacing from a few millimeters to several tens of meters in spacing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Shortcomings in seismic images of folds== | ||
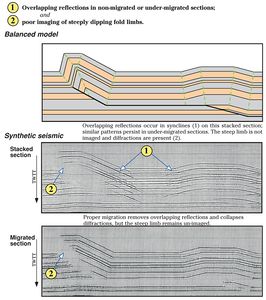
| + | Folds can be distorted or only partially imaged in seismic sections. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery mode=packed heights=200px widths=200px> | ||
| + | File:ST53_Part01_Pg06A.jpg|{{figure number|6}} | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Locating axial surfaces in seismic sections== | ||
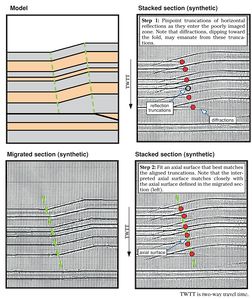
| + | Migration moves dipping reflections upward and laterally to properly image the fold geometry, but reflections on non-migrated or under-migrated sections do not accurately represent fold shape. However, axial surfaces can be inferred on these sections by mapping the truncations of horizontal reflections. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery mode=packed heights=200px widths=200px> | ||
| + | File:ST53_Part01_Pg06B.jpg|{{figure number|7}} | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Interpreting folds in poorly imaged zones== | ||
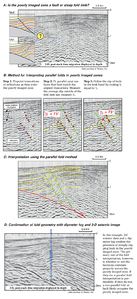
| + | Poorly imaged zones on folds are commonly caused by, and interpreted as, faults or steep limbs. Both solutions are often permissible and should be evaluated. In [[:file:ST53_Part01_Pg07.jpg|Figure 8]], a method of interpreting parallel folds in poorly imaged zones is described. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <gallery mode=packed heights=200px widths=200px> | ||
| + | File:ST53_Part01_Pg07.jpg|{{figure number|8}} | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
Latest revision as of 15:09, 18 January 2016
| Seismic Interpretation of Contractional Fault-Related Folds: An AAPG Seismic Atlas | |

| |
| Series | Studies in Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Part 1 |
| Chapter | Structural Interpretation Methods |
| Author | John H. Shaw, Christopher D. Connors, and John Suppe |
| Link | Web page |
| PDF file (requires access) | |
| Store | AAPG Store |
Folds are bends or flexures of layered rock that form in response to motion along faults, diapirism, compaction, and regional subsidence or uplift. Folds are expressed in seismic reflection profiles as one or more regions of dipping reflections (dip domains) that correspond to inclined stratigraphic contacts.
Dip domains are separated by axial surfaces; imaginary planes which, when viewed in two dimensions, form axial traces. Anticlinal axial surfaces occupy concave-downward fold hinges; synclinal axial surfaces occupy concave-upward fold hinges.
Folds and bedding thickness
Folds are classified based on whether or not the thickness of stratigraphic layers changes in dip domains or across axial surfaces.
Parallel folds preserve layer thickness, and are common in strata that deformed predominantly by flexural slip (see inset at right on Figure 4). Axial surfaces bisect inter-limb angles in parallel folds.
Parallel folds commonly form by a deformation mechanism called flexural slip, where folding is accommodated by motions on minor faults that occur along some mechanical layering—usually bedding. Flexural-slip surfaces, which can be observed in core or outcrop, may vary in spacing from a few millimeters to several tens of meters in spacing.
Shortcomings in seismic images of folds
Folds can be distorted or only partially imaged in seismic sections.
Locating axial surfaces in seismic sections
Migration moves dipping reflections upward and laterally to properly image the fold geometry, but reflections on non-migrated or under-migrated sections do not accurately represent fold shape. However, axial surfaces can be inferred on these sections by mapping the truncations of horizontal reflections.
Interpreting folds in poorly imaged zones
Poorly imaged zones on folds are commonly caused by, and interpreted as, faults or steep limbs. Both solutions are often permissible and should be evaluated. In Figure 8, a method of interpreting parallel folds in poorly imaged zones is described.