Mudlogging: the mudlog
| Development Geology Reference Manual | |

| |
| Series | Methods in Exploration |
|---|---|
| Part | Wellsite methods |
| Chapter | Mudlogging: the mudlog |
| Author | Alun Whittaker |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
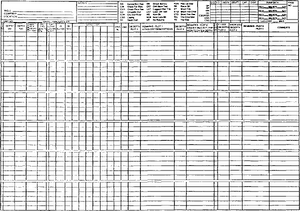
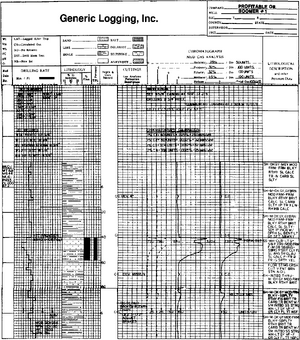
Information gathered by the mudlogging crew is first recorded on a data sheet (Figure 1) and then plotted onto a mudlog form (Figure 2). Each mudlogger is responsible for plotting the data acquired during his or her tour. In this way, the mudlog becomes an accurate and up-to-date record of nearly all activity related to the drilling of the well.
It is very important that a mudlog be recorded on a standard format using standardized plotting and reporting procedures. This is necessary to allow valid and convenient comparison of log data from well to well and to prevent confusion or misunderstanding over the meaning of a log trace or annotation.
Layout of A mudlog
Figure 2 is an example of the layout and information content of a standard mud log. The general usage of the tracks (columns) on a mudlog are outlined here.
Log headings
The log heading identifies mudlog and records parameters used in preparing the log. The various headings are as follows:
- Operator and well name
- Location
- Rig name and type
- Elevations
- Dates and times
- Mudlogging company and crew
- Other mudlogging services
- Casing sizes and depths
- Mud type and characteristics
- Mudlog symbols and abbreviations
- Gas calibration information
Track 1: Rate of Penetration (ROP)
This track gives a relative indication of rock strength and porosity. Track 1 includes the following information:
- ROP and normalized ROP (NROP) (see chapter on “Rate of Penetration”)
- Bit number, type, and diameter
- Number and size of jets
- Bit run (time per feet drilled)
- Bit grade (wear and damage)
- Weight on bit
- Rotary speed
- Mud (standpipe pressure and flow rate)
Track 2: cuttings lithology
Track 2 identifies and records the lithology of the cuttings material that arrives at the surface as drilling takes place (see chapter on Mudlogging: Drill cuttings analysis). Information is commonly presented as lithological symbols, each representing 10% of the total sample volume. This is commonly referred to as a percentage log.
Some mudlog formats have an interpreted lithology column adjacent to the percent lithology. This interpreted lithology log attempts to take into account factors that might affect cuttings recovery, such as sloughing and trips.
Additional reservoir information can also be recorded in track 2. In the example log shown in Figure 2, a separate column is included for qualitative porosity estimation.
Track 3: depth annotation
Depths are noted in track 3 using the traditional scales (in the United States) of length::2 in. to length::100 ft (1:600) and length::5 in. to length::100 ft (1:240). This track also includes the location (depth or interval) of the following:
- Conventional cores
- Sidewall cores
- Drill stem tests (DSTs)
- Wireline formation tests
Tracks 4 and 5: hydrocarbon evaluation
These two tracks consist of the following information:
- Total combustible hydrocarbons from gas trap, mud, cuttings blender tests, and nonformational borehole gas events such as trip gas, carbide lag checks, and connection gas are recorded.
- Hydrocarbon chromatograph with gaseous alkanes (methane, ethane, propane, butanes, and pentanes) are plotted as individual tracks. Chromatograph calibration checks are also included, providing they do not obscure well data.
- Oil evaluation includes subjective and qualitative evaluation of oil staining and solvent-cut oil. (Many mudloggers include these data in the lithology track.) This evaluation can also include qualitative analysis of oil fluorimetry, refractometry, and geochemistry.
Track 6: geological and lithological evaluation
Track 6 is subdivided into the following categories:
- Mineralogy and geochemical analyses
- Interpreted lithology log
- Lithological descriptions
- Comments, which include special analyses, reports of borehole conditions, and reports of drilling events that have an effect on overall log interpretation (such as loss of returns and power failure)
See also
- Introduction to wellsite methods
- Mudlogging: drill cuttings analysis
- Drilling fluid
- Mudlogging: equipment, services, and personnel
- Mudlogging: gas extraction and monitoring