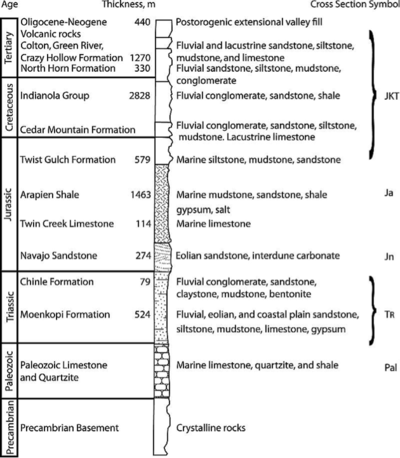
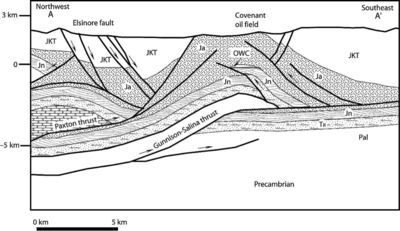
Covenant field
The Covenant Field is an oil field located in Sevier County, Utah. The field was discovered in 2004 by Wolverine Oil and Gas, in the Kings Meadow Ranches #17-1 well when it encountered oil in the Navajo Formation . Credits for the geologic ideas behind the discovery have been attributed to Dr. Douglas K. Strickland. The work leading to this discovery is has been summarized by Strickland in several presentations at AAPG conferences. (S&D 2005, and the video in 2007)
Structure
The Covenant field is located in the central Utah thrust belt. Chidsey, et. Al. 2007, describe the Covenant field trap as an “elongate, symmetric, northeast-trending, fault-propagation/fault-bend anticline with nearly 800 feet (270m) of structural closure with a 450-foot (150M) oil column. The oil-charged Navajo reservoir covers about 960 acres”. The structure is related to movement along the Gunnison-Salina thrust and Paxton thrust fault and part of the larger Utah thrust belt province, this is outlined in greater detail by Chidsey, et. Al 2007.
Reservoir
The primary (as of 2007?) reservoir in the Covenant Field is the Navajo Sandstone Early Jurassic (Toarcian) eolian sandstone. Parry, Chan, and Nash, 2009 outlined diagenetic charchteristics of the Navajo Sandstone from cores in the Covenant field. As of April 2015 the field had 24 active wells, and had produced a cumulative 21,443,660 barrels of oil. https://oilgas.ogm.utah.gov/pub/Publications/Reports/Prod/Field/?C=M;O=D
Significance
The significance of the Covenant discovery, summarized by Chidsey, is that it proved that the central Utah thrust belt contained the right components of trap, reservoir, seal, source and migration history for large accumulations of oil to occur. In reflecting on the exploration work leading to its discovery Strickland, 2005, noted that the Covenant field disproved many aspects of conventional wisdom as to the exploration potential of the region.
References
Strickland, D., Johnson, K.R., Vrona, J.P., Schelling, D.D., and Wavrek, D.A., 2005, Structural architecture, petroleum systems, and geological implications for the Covenant field discovery, Sevier County, Utah: Online, American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Search and Discovery Article No. 110014,
Central Utah: Diverse Geology of a Dynamic Landscape, 2007 Pages 273-296 Petroleum Geology of Covenant Oil Field, Central Utah Thrust Belt Thomas C. Chidsey Jr.1, Jacob S. DeHamer2, Emily E. Hartwick3, Keith R. Johnson4, Daniel D. Schelling5, Douglas A. Sprinkel6,Douglas K. Strickland7, John P. Vrona8, David A. Wavrek
AAPG Bulletin, V. 93, No. 8 (August 2009), P. 1039-1061. DOI:10.1306/04270908170 Diagenetic characteristics of the Jurassic Navajo Sandstone in the Covenant oil field, central Utah thrust belt W. T., Parry,1 Marjorie A. Chan,,2 Barbara P. Nash3
_________________________ Eolian Architecture of Sandstone Reservoirs in the Covenant Field, Sevier County, Utah; #20091 (2010) Emily E. Hartwick Search and Discovery.com
Conventional Wisdom: A Different Approach„Exploration in the Central Utah Thrust Belt Doug Strickland Search and Discovery.com
Conventional Wisdom: A Different Approach„Exploration in the Central Utah Thrust Belt 2009 Audio-Video presentations at 2009 AAPG Annual Convention, Denver, Colorado, June 7-10, 2009 Or - http://player.piksel.com/player.php?v=bl432u69 Search and Discovery.com
http://www.aapg.org/publications/news/explorer/emphasis/articleid/11089/tricky-geology-is-utah-hallmark Not sure if this is the latest explorer article or not?