Search results
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Page title matches
- ==Karst environment== ...rainage. Karst has unique hydrology condition, this condition is caused of karst composed of soluble lithology and the lithology has good condition in secon13 KB (2,016 words) - 19:56, 5 April 2019
File:UDip Karst Fig 1.png (453 × 282 (37 KB)) - 20:13, 1 July 2015
File:UDip Karst Fig 2.png (708 × 390 (26 KB)) - 20:21, 1 July 2015
File:UDip Karst Fig 3.png (693 × 276 (114 KB)) - 20:21, 1 July 2015
File:UDip Karst Fig 4.png (656 × 368 (119 KB)) - 20:21, 1 July 2015
File:UDip Karst Diagram 1.png (557 × 618 (51 KB)) - 20:22, 1 July 2015
Page text matches
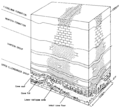
File:Carbonate-reservoir-models-facies-diagenesis-and-flow-characterization fig4.png Schematic diagram of the karst-collapse reservoir model showing three karst facies. (From Kerans, 1989.)(1,827 × 1,643 (189 KB)) - 19:02, 13 January 2014- ==Karst environment== ...rainage. Karst has unique hydrology condition, this condition is caused of karst composed of soluble lithology and the lithology has good condition in secon13 KB (2,016 words) - 19:56, 5 April 2019
- ** [[Karst]]2 KB (215 words) - 20:43, 10 August 2015
- ...estroyed by [[paleosol]]s, [[Meteoric diagenesis|meteoric cementation]], [[karst]]ing, cave development, and/or sediment infill2 KB (294 words) - 21:01, 4 February 2022
- ...y]] and flow characteristics are totally controlled by diagenesis, as in [[Karst|karsted]] reservoirs. ...pratidal]] [[dolomitization]] and [[sulfate]] emplacement model, (3) the [[karst]]-collapse model, and (4) the geological [[reef]] model.23 KB (3,026 words) - 20:48, 19 January 2022
- * [[Karst topography]]3 KB (399 words) - 12:51, 28 September 2015
- ...rugged mountainous terrain, dense equatorial jungle, and thick, heavily [[karst]]ified [[limestone]]. The karstified limestone in some areas is also overla4 KB (520 words) - 15:12, 31 January 2022
- ...ched (secondary) porosity || Subunconformity diagenesis || Dissolving || [[Karst]] and cavern formation5 KB (645 words) - 16:14, 13 April 2022
- * [[Karst]]5 KB (543 words) - 23:45, 8 January 2015
- * Karst,4 KB (584 words) - 21:29, 13 October 2014
- ...; therefore, vuggy porosity and [http://wiki.seg.org/wiki/Dictionary:Karst karst] features are common.7 KB (894 words) - 20:54, 6 April 2022
- ...rm karsting tend to be highly compartmentalized<ref name=ch09r50 /> Vadose karst reservoirs tend to be of poor quality contrasted with phreatic reservoirs,7 KB (960 words) - 21:00, 6 April 2022
- #* Facies on shelf reflect inherited topography form the lowstand (e.g., karst) and transgression (e.g., build-ups)8 KB (1,084 words) - 22:25, 3 February 2022
- # karst; and ...be mappable on 3-D seismic data. Collapse and sag structures form circular karst features that may be discernable from amplitude displays.<ref>Loucks, R. G.38 KB (5,571 words) - 15:31, 16 January 2024
- ...with or without the breakdown of this appearance (associated with cave and karst generally) and the solution which increases the interparticle porosity. Thi16 KB (2,395 words) - 21:18, 9 January 2024
- ...mineral / rock but it can also be formed in continental environments e.g., karst and lakes (Baldermann et al., 2020). There can be primary and secondary dol ...J.A.D., Fallick, A.E., Keppens, E., 1997. Spheroidal dolomites in a Visean karst system-bacterial induced origin. Sedimentology, 44, 177-195.38 KB (4,996 words) - 21:07, 21 April 2022
- ...carbonate reservoirs, unconformities can dramatically dissolve and create karst reservoir fabrics.<ref name=Derbyetal_2012>Derby, J., R. Fritz, S. Longacre27 KB (3,791 words) - 19:35, 11 October 2022