Coal bed methane (UB)
Preface
Coal Bed Methane (CBM) is unconventional natural gas which come from coal. CBM can be used as energy alternative beside hidrocarbon. Coal that used as source CBM provides 25% world energy. CBM resources predicted about 9000 TCF, mainly in North America (3000 TCF) and other country former Soviet Union (4000 TCF). CBM fistly used around coal mining. Coal mines can simultaneoustly produce methane and consume it by generating electricity. The electricty can be used to operate many instrument in around coal mining. Then electicity from CBM can be selling to power supplier for cost recovery in coal mines.
Origin of Coal
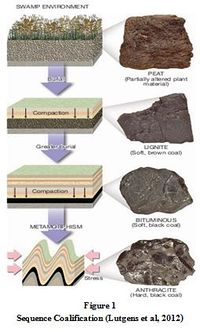
Coal is sedimentary rock which rich organic material that compaction with coalification process. Coal construct in environment with low oxygen content, such as swamp or bogs. Coal easily known because has black colour. Furthermore, if saw under microschope will be seen remain plant that not fully decay, such as leaves and root.
Initially coal formation construct when acumulation plant remains with an-oxic condition, so plant can not decaying. The environment that poor with oxygen is swamp. Instead, the plants are attacked by bacteria that partly decompose th organic material and liberate oxygen and hydrogen. When that elemen come out, the percentage of carbon increase. Bacteria cannot fully decompose organic material because they are destroyed by acids liberated from plants.[2]
Plant remains acumulation built a peat which plant material easily known. Then peat slowly change to lignite (brown coal), which is early stage of coal formation. Because burial condition, it make pressure and temperature increase. This increases make chemical reaction, this reaction making coal losing water and gas and increasing carbon concentration. Lignite then become bituminus coal which have higher carbon concentration. If pressure and temperature increase coal bituminus become antracite, black coal with higest carbon concentration.
Coal classified by degree of coalification (increasing organic carbon content) in terms coal rank (Table 1). Lignite and sub bituminus are low rank coal with low carbon content. Bituminus is midde rank and the higgest rank coal are known as antracite which has highest carbon concentration. [3]
Gas in CBM
Most CBM has been produced by microbial, thermal, or possibly catalytic degradation of organic material present in coal. CBM is mainly composed of methane (CH4) with variable additions of carbon dioxide (CO2), elemental nitrogen (N2), and heavier hydrocarbon, such as ethane (C2H6), and trace of propane (C3H8) and butanes (C4H10).[5]
CBM Storage
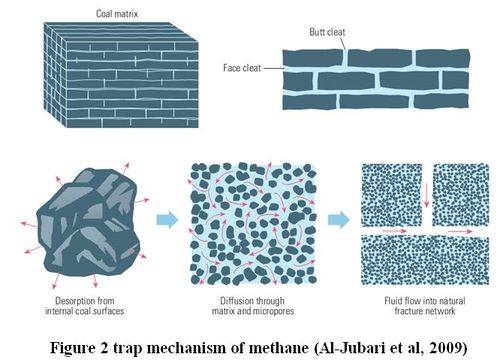
Trap mecanism of CBM different with gas conventional. In gas conventional, gas trap in porosity of rock. But in CBM, methane trap in microporosity of coal. This microporosity have capasity to store gas six times more than conventional gas. This microporosity created when coal began coalification process. When temperature and pressure of coal increase, matrix in coal decrease create micro pore that trap methane. The increase fracture also making fracture or cleats in coal, so making permeability in coal (Figure 2).
CBM Production
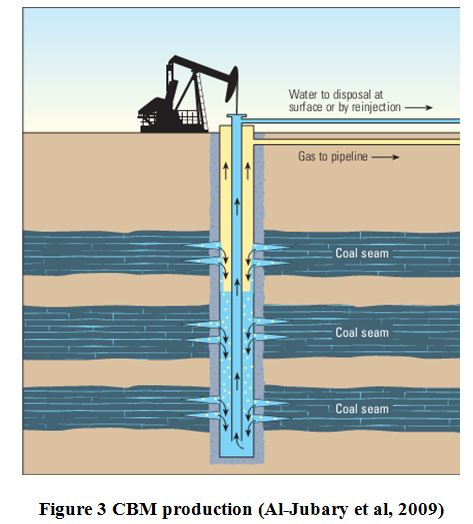
Methane which trapped in microporosity can be production by dewatering. Dewatering is process to displace methane with using water. Methane pulled to well bore with decreasing formation pressure. Water than moving into well bore with methane inside of water. And then water and methane separated, methane will be save in storage and water will be injected again to subsurface. CBM has slow rate production. To increase production usually stimulated with hidrolic fracture to increase permeability of coal (Figure 3).
Future CBM
CBM in future has many economic potential. It can be used to generate electricity. Not only around the coal mining site but also can be pipelined for utility and industrial use. Electricity can be selling to power supplier to be piped to other town. Some of CBM potential is already realized.
References
- ↑ Carlson et al. 2008. Physical Geology: Earth Revealed. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
- ↑ Lutgens et al. 2012. Essential of Geology. USA: Pearson Prentice Hall
- ↑ Nichols, Gary. 2009. Sedimentology and Stratigraphy. United Kingdom: A John Wiley & Son, Ltd
- ↑ Carlson et al. 2008. Physical Geology: Earth Revealed. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
- ↑ Thakur et al. 2014. Coal Bed Methane – from Prospect to Pipeline.Elsevier
- ↑ Al-Jubary et al. 2009. Oilfield Review Summer 2009.21: Schlumberger
- ↑ Al-Jubary et al. 2009. Oilfield Review Summer 2009.21: Schlumberger
Source
Al-Jubary et al. 2009. Oilfield Review Summer 2009. 21: Schlumberger.
Carlson et al. 2008. Physical Geology: Earth Revealed. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies.
Iskhakov, Ruslan. 2013. Coal Bed Methane. Publised on http://large.stanford.edu/. Accesed June 28th, 2015.
Lutgens et al. 2012. Essential of Geology. USA: Pearson Prentice HallTM.
Nichols, Gary. 2009. Sedimentology and Stratigraphy. United Kingdom: A John Wiley & Son, Ltd.
Thakur et al. 2014. Coal Bed Methane – from Prospect to Pipeline. Elsevier