Difference between revisions of "How to plot the strike data to the Rosette diagram"
Dimassyafii (talk | contribs) |
Dimassyafii (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
# Read either end of the compass needle to obtain the value of strike. | # Read either end of the compass needle to obtain the value of strike. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:measure strike.png|framed|center|Figure.5 Measure strike with Brunton Compass<ref>http://courses.geo.ucalgary.ca/glgy203/images/sd.htm.<ref/>]] |
=Rosette Diagram= | =Rosette Diagram= | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
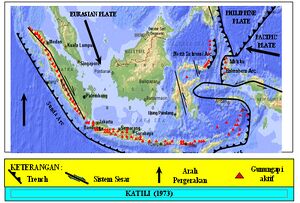
Two main force compress the rock between them, so the rock become stress. The main force that come from N7o E is resultant force between Eurasian Plate and Pacific Plate. Then the main force that come from N97o E is resulted by Indo-Australia (see Figure 8). So, the result of strike measurement in Karangsambung agree with fact. | Two main force compress the rock between them, so the rock become stress. The main force that come from N7o E is resultant force between Eurasian Plate and Pacific Plate. Then the main force that come from N97o E is resulted by Indo-Australia (see Figure 8). So, the result of strike measurement in Karangsambung agree with fact. | ||
| − | [[File:Gaya utama Indonesia.jpg|thumbnail|Figure 8. Plate tectonic around Indonesia | + | [[File:Gaya utama Indonesia.jpg|thumbnail|Figure 8. Plate tectonic around Indonesia]] |
=Reference= | =Reference= | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
Revision as of 04:47, 1 July 2015
Definition
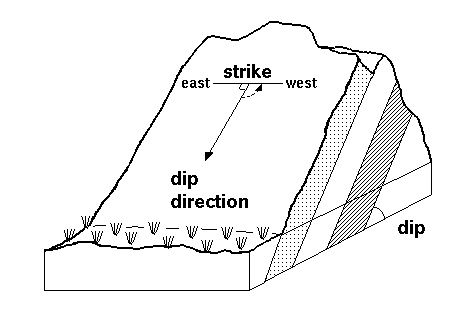
The orientation of a rock bed, fault, fracture, cuestas, igneous dikes, and sills can be described using strike and dip of the rock. Strike is direction of the line formed by the intersection of a fault, bed, or other planar feature and a horizontal plane. Strike indicates the attitude or position of linear structural features such as faults, beds, joints, and folds. Dip is the angle at which a planar feature is inclined to the horizontal plane; it is measured in a vertical plane perpendicular to the strike of the feature.[1]
Brunton Compass
Usually the direction of strike and dip can be determined easily with left hand rule. They also can be measured accurately with Brunton Compass. Parts of Brunton Compass explained by Figure 2:
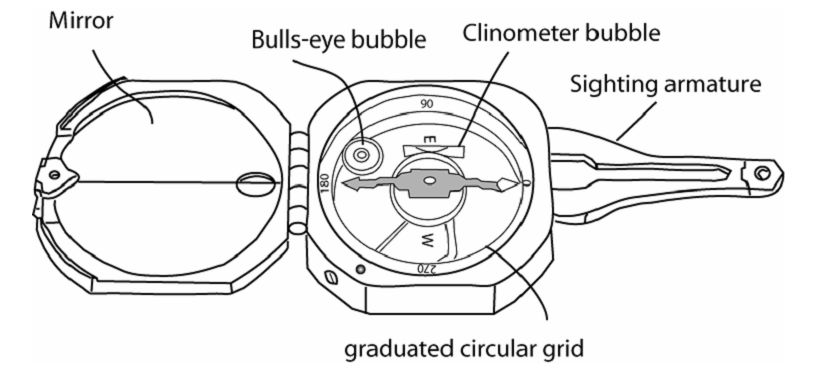
Brunton Compass can be used for:
- Measure strike and dip of planes
- Measure trend and plunge of lines
- Measure vertical angles
- Measure bearings
- Set local declination[3]
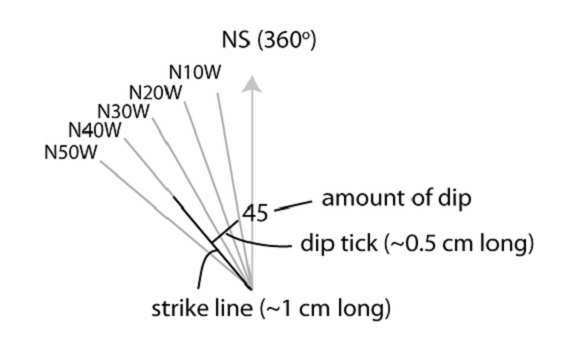
In determine the direction of strike and dip, there are four quadrants at Brunton Compass such as North East, North West, South East, and South West. Each of them have value 0-90 degree. For example in Figure 3, N40o W mean the direction of strike is 40o from North to West. 45o is amount of dip. The direction of dip always perpendicular with direction of strike, so we know the direction of dip is N50o E.
How to Measure Strike
To measure strike of rock we can used Brunton Compass. The steps are:
- Place the bottom EDGE of the compass flat against the plane of interest. (The direction of sighting armature follow the direction of strike)
- Adjust the compass orientation, making sure the bottom edge is always flat against the plane (Sometimes it is easier to put your field book against the outcrop and then the compass against the book to get a smoother and/or a larger surface), until the air bubble in the "Bull's eye level" is centered.
- Read either end of the compass needle to obtain the value of strike.
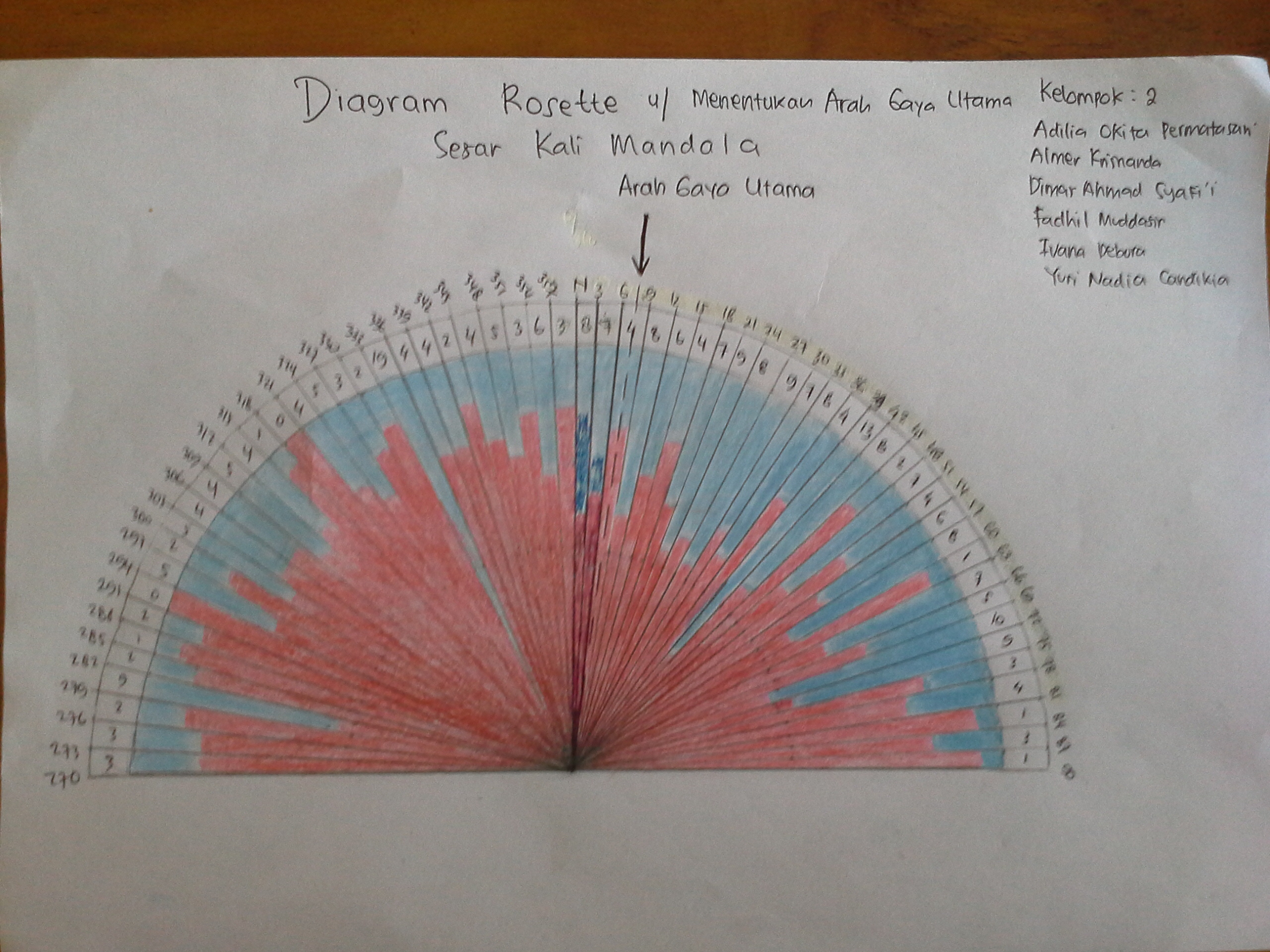
</ref> missing for <ref> tagThe radial histogram in rosette diagram (the yellow one on Figure 6) show the direction of strike.
Case Study
Indonesia is a country located between three major plates, there are Eurasian Plate, Indo-Australia Plate and Pacific Plate. Eurasian Plate have opposite moving direction with Indo-Australia Plate. Eurasian Plate have moving direction about Base rock of Java Island is claystone. At Karangrangsambung, Kebumen, Center of Java, there are outcrops of claystone, base rock of Java Island, it is called Karangsambung Formation. On June 16, 2015 Geophysics of University of Indonesia held Field Trip to Karangsambung, and observed strike of claystone at Kalimandala Karangsambung. The result of the observation is:
From data above we find the dominant angel at NE quadrant is 39 – 42 degree, and at NW quadrant is 333 – 336 degree. 39 – 42 and 333 – 336 area form angel 60o, to determine the main force we have to find the center of 39 – 42 and 333 – 336 area, it will be 7o (see Figure 7). So the main force come from N7o E and N97o E. There are two main force that have opposite direction.
Two main force compress the rock between them, so the rock become stress. The main force that come from N7o E is resultant force between Eurasian Plate and Pacific Plate. Then the main force that come from N97o E is resulted by Indo-Australia (see Figure 8). So, the result of strike measurement in Karangsambung agree with fact.