Difference between revisions of "User:10112132/Sandbox"
(Geological Map) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | <big>'''Preface'''</big> | |
In geological field, maps which were generated from data whom researchers had collected which then would be portrayed onto a basic map -which in general gives information about Earth’s reliefs interpretation- and then described on a flat plane, called geological map. Geological maps give informations about geological conditions on particular area which includes rocks units and its structures. From geological map, we can obtain type of rocks, thickness, lithologies bearings (strike and dips), faults, folds, fractures, or many processes have had occured on earlier time. | In geological field, maps which were generated from data whom researchers had collected which then would be portrayed onto a basic map -which in general gives information about Earth’s reliefs interpretation- and then described on a flat plane, called geological map. Geological maps give informations about geological conditions on particular area which includes rocks units and its structures. From geological map, we can obtain type of rocks, thickness, lithologies bearings (strike and dips), faults, folds, fractures, or many processes have had occured on earlier time. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
==How To Make Geological Map== | ==How To Make Geological Map== | ||
| − | The main equipment needed to do geological mapping is: | + | <big>The main equipment needed to do geological mapping is:</big> |
# Base Map: is used to show an overview of the area that will be mapped. | # Base Map: is used to show an overview of the area that will be mapped. | ||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
# GPS: is used to determine the outcrop location. | # GPS: is used to determine the outcrop location. | ||
| − | The steps to do geological mapping activity is: | + | <big>The steps to do geological mapping activity is:</big> |
| + | |||
# We make outcrop observation, and make a description of it. | # We make outcrop observation, and make a description of it. | ||
# We measure the position of rocks (strike and dip), geological structure elements, and other geological elements. | # We measure the position of rocks (strike and dip), geological structure elements, and other geological elements. | ||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
# We Determine the outcrop location by using GPS. | # We Determine the outcrop location by using GPS. | ||
| − | Steps to create geological maps: | + | <big>Steps to create geological maps:</big> |
| + | |||
# Make Geological Maps Framework | # Make Geological Maps Framework | ||
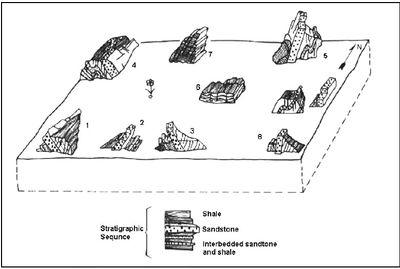
| − | Geological maps | + | Geological maps framework is a set of data that is used to the process of makinga map. The contents is:, symbols of station number (track); types of rock symbol; Plotting symbol of strike/dip; Plotting symbol of structure element. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:1.jpg|400px|thumbnail|center|Figure 1 Lithology of Outcrop and Field Structure Sketch]] | ||
| + | |||
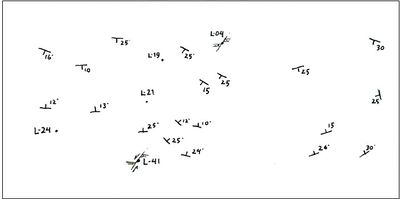
| + | # Make a Strike and Dip Map | ||
| + | This map shows the plots of strike and dipfrom a region. In the reconstruction, it necessary some step: | ||
| + | * Inventory a required data, such as strike and dip, and the description ofrockintorock unitsalong withits contacts as well asan indication ofthe geologicalstructures(faults, folding) | ||
| + | * Plotting data on the map. we make a contour map based on the similarity towards the strike and dip of outcrops were obtained. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:2.jpg|400px|thumbnail|center|Figure 2 Strike/Dip Data Plot and Indication of Geology Structure]] | ||
| + | |||
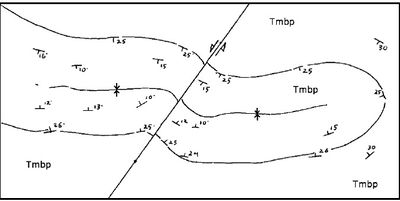
| + | * How to reconstruct the pattern of strike of the rock layering pattern is as follows: plot the data needed; create key strike/dip contour; reconstructs the geological structure if any; and reconstructs the pattern of strike and dip. | ||
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:3.jpg|400px|thumbnail|center|Figure 3 Data Plot on 25°]] |
Revision as of 04:55, 30 June 2015
Preface
In geological field, maps which were generated from data whom researchers had collected which then would be portrayed onto a basic map -which in general gives information about Earth’s reliefs interpretation- and then described on a flat plane, called geological map. Geological maps give informations about geological conditions on particular area which includes rocks units and its structures. From geological map, we can obtain type of rocks, thickness, lithologies bearings (strike and dips), faults, folds, fractures, or many processes have had occured on earlier time.
History of Geological Map
William Smith (1769), a British engineer known as a pioneer of stratigraphy, createda very useful geology maps and illustrated the distribution of rocks on a topographic map. The idea of making original map of rocks distribution was coined in 1684 by Martin Lister (1639-1712). Lister stated that the distribution of different types of British landscape could be accurately represented on topographic maps.
”The Soil might either be coloured, by variety of Lines, or Etchings; but the great care must be, very exactly to note upon the Map”
Which Lister concluded that the soil types mapping can also maps the distribution of rocks in the subsurface. Yet, the next important stage from Lister is not continued.
Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli (1658-1730) created topographic maps for military use of the visited countries (Italy, France, Germany, the Balkans, and Turkey). Marsigli published a mining district map in Hungary and sketched the distribution of sulfur near his hometown, Bologna (1717). Probably, the first geological map drawn by an anonymous naval cartographer in 1757 where in the Heligoland islands he added boundaries of four different types of rocks.
Types of Geological Map
Geological map is divided into several types:
- Surface Geological Map, is a map that contains geological information below the surface. This map has various scale from 1:50.000 or greater than that.
- Outcrop map , is a map that contains about the discovery of the location of the rock. These map provide information about rock properties and its structure condition. This type of map are generally in large scale.
- Overview Geological Map, is a map that give information about formation which has been revealed, As well as the location of the extrapolation of formation is still covered by a layer of Holocene. This map is usually have scale from 1:100.000 or smaller than that.
- Structure Map, is a map which the appearance of the depth lines to explain certain layer under the surface.This kind of map has a medium to large scale.
- Schematic geological map, is a map that contains geological data based on topography map.
- Thematic geological map, is a map that contains geological information about natural resources and potential energy in certain location.
- Topography map, is maps showing the height of a region in the form of contour height measured against the average sea level.
- Isopach Map, is a map which represent lines that connect a formation or a layer with the same thickness without sctructural needed. This map generally has a medium to large scale.
- Photogeological Map, is a map creates based on the result of aerial photographs that adapted to the actual condition on field.
- Hydrogeological Map, is a map showing the condition of ground water in certain location and it is known whether the formation is permeable or impermeable.
How To Make Geological Map
The main equipment needed to do geological mapping is:
- Base Map: is used to show an overview of the area that will be mapped.
- Compass and Clinometer: is used to measure the strike and dip from a rocks and geological structure.
- Stationery and field notebook: is used to record and describe the characteristic of rocks was found at the observation location.
- Hammers and Chisels: is used to take rocks samples.
- Hand lens: is used to observe the characteristics of rock that cannot be seen with the eye directly, such as the grain size and others
- Gauge: is used is used to determine the length of an outcrop or structure.
- GPS: is used to determine the outcrop location.
The steps to do geological mapping activity is:
- We make outcrop observation, and make a description of it.
- We measure the position of rocks (strike and dip), geological structure elements, and other geological elements.
- We make a record observations in a field notebook
- We Determine the outcrop location by using GPS.
Steps to create geological maps:
- Make Geological Maps Framework
Geological maps framework is a set of data that is used to the process of makinga map. The contents is:, symbols of station number (track); types of rock symbol; Plotting symbol of strike/dip; Plotting symbol of structure element.
- Make a Strike and Dip Map
This map shows the plots of strike and dipfrom a region. In the reconstruction, it necessary some step:
- Inventory a required data, such as strike and dip, and the description ofrockintorock unitsalong withits contacts as well asan indication ofthe geologicalstructures(faults, folding)
- Plotting data on the map. we make a contour map based on the similarity towards the strike and dip of outcrops were obtained.
- How to reconstruct the pattern of strike of the rock layering pattern is as follows: plot the data needed; create key strike/dip contour; reconstructs the geological structure if any; and reconstructs the pattern of strike and dip.
Other stuff
Cite is done![1]