Surficial geochemical case history 2: stratigraphic trap
| It has been suggested that this article be merged with [[::Surficial geochemical case histories|Surficial geochemical case histories]]. (Discuss) |
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps |
| Chapter | Surface geochemical exploration for petroleum |
| Author | Dietmar Schumacher |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
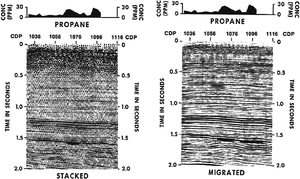
In this case history, the client conducted a soil gas hydrocarbon survey along the trace of the seismic line to look for evidence of hydrocarbon microseepage from a seismically defined trap at commom depth point (CDP) 1070 (Figure 1). Propane soil gas anomalies were detected at CDP 1070 and 1096. The wildcat well drilled at CDP 1070 resulted in a new field discovery. The geochemical lead at CDP 1096 was reevaluated seismically. After additional processing, a revised interpretation (right) also predicted porosity development there and coincident with the surface geochemical anomaly. A second productive well was drilled at CDP 1096.
Figure 1 is a seismic section and soil gas profile of a stratigraphic trap located at approximately depth::5,600 ft (1.5 sec) in the Cretaceous Escondido Sandstone in La Salle County, Texas.
See also
- Geochemical case histories
- Surficial geochemical case history 1: structural traps
- Surficial geochemical case history 3: Predrill–postdrill comparison
References
- ↑ Rice, G., 1989, Exploration Enhancement by integrating near-surface geochemical and seismic methods: Oil & Gas Journal, v. 87, no. 14 (April 3), p. 66-71.