Difference between revisions of "Subregional and local pressure compartments"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
Cwhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
Cwhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==Subregional pressure compartments== | ==Subregional pressure compartments== | ||
| − | <gallery mode=packed widths= | + | <gallery mode=packed widths=300px heights=300px> |
formation-fluid-pressure-and-its-application_fig5-26.png|{{figure number|1}}. | formation-fluid-pressure-and-its-application_fig5-26.png|{{figure number|1}}. | ||
formation-fluid-pressure-and-its-application_fig5-25.png|{{figure number|2}}. | formation-fluid-pressure-and-its-application_fig5-25.png|{{figure number|2}}. | ||
Revision as of 13:29, 3 July 2014
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Critical elements of the petroleum system |
| Chapter | Formation fluid pressure and its application |
| Author | Edward A. Beaumont, Forrest Fiedler |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
Subregional or local (second- and third-order) pressure compartments can be found within normal pressure regimes or regional pressure compartments.
Subregional pressure compartments
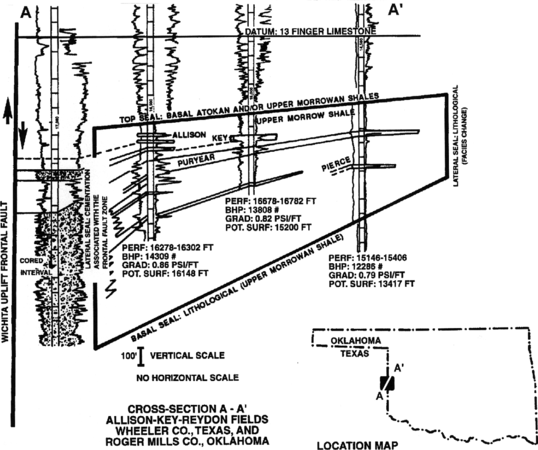
Figure 1 is an example of a subregional compartment contained within the regional pressure compartment of the Anadarko basin of Figure 2.
Local pressure compartments
The fluids in a porous bioherm completely encased in shale (as shown in Figure 3) are virtually isolated from the nearby fluid systems outside the bioherm. The bioherm, then, is a pressure compartment that may or may not be abnormally pressured. Other geological features that may form local pressure compartments are fault blocks, sand lenses, and sand wedges developed in growth faults.
See also
- Pressure compartments
- Regional pressure compartments
- Pressure compartment seals
- Applying pressure compartment concepts to exploration