Difference between revisions of "Free water level determination using pressure"
(Initial import) |
(formatting) |
||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| 1 | | 1 | ||
| − | | Determine buoyancy pressure (P<sub>b</sub> ) at the depth of the measured pressure (P<sub>m</sub> ) from the measured pressure: | + | | Determine buoyancy pressure (''P''<sub>b</sub> ) at the depth of the measured pressure (P<sub>m</sub> ) from the measured pressure: |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math>P_{\rm b} = P_{\rm m} - P_{\rm hydrostatic}</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| 2 | | 2 | ||
| − | | Determine buoyancy pressure gradient (P<sub>bg</sub> ): | + | | Determine buoyancy pressure gradient (''P''<sub>bg</sub> ): |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math>P_{\rm bg} = P_{\rm hydrostatic\ pressure\ gradient} - P_{\rm hydrocarbon\ pressure\ gradient}</math> |
|- | |- | ||
| 3 | | 3 | ||
| − | | Calculate downdip length of hydrocarbon column (h): | + | | Calculate downdip length of hydrocarbon column (''h''): |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math>h = \frac{P_{\rm b}}{P_{\rm bg}}</math> |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
As an example, let's determine the downdip length of a 30°API oil column with the following givens: | As an example, let's determine the downdip length of a 30°API oil column with the following givens: | ||
| − | * P<sub>m</sub> = 3555 psi at 7611 ft | + | * ''P''<sub>m</sub> = [[pressure::3555 psi]] at [[depth::7611 ft]] |
| − | * P<sub>hydrostatic</sub> = 3525 psi | + | * ''P''<sub>hydrostatic</sub> = 3525 psi |
| − | * P<sub>hydrostatic pressure gradient</sub> = 0.465 psi/ft | + | * ''P''<sub>hydrostatic pressure gradient</sub> = 0.465 psi/ft |
| − | * P<sub>hydrocarbon pressure gradient</sub> = 0.38 psi/ft | + | * ''P''<sub>hydrocarbon pressure gradient</sub> = 0.38 psi/ft |
'''Answer''' (tied back to steps above): | '''Answer''' (tied back to steps above): | ||
| − | + | :<math>P_{\rm b} = P_{m} - P_{\rm hydrostatic} = 3555 - 3525 = 30\ \mathrm{psi}</math> | |
| − | :<math> | + | :<math>P_{\rm hydrostatic\ pressure\ gradient} - P_{\rm hydrocarbon\ pressure\ gradient} = 0.465 - 0.38 = 0.085 \mbox{ psi/ft}</math> |
| − | + | :<math>h = \frac{P_{\rm b}}{P_{\rm bg}} = 30 \mbox{ psi} \div 0.054 \mbox{ psi/ft} = 556 \mbox{ ft}</math> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | :<math> | ||
Therefore, the free-water level is at [[depth::8167 ft]]. | Therefore, the free-water level is at [[depth::8167 ft]]. | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 30 January 2014
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Critical elements of the petroleum system |
| Chapter | Formation fluid pressure and its application |
| Author | Edward A. Beaumont, Forrest Fiedler |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
The free-water level occurs where buoyancy pressure is zero in the reservoir-aquifer system. It defines the downdip limits of an accumulation. Pressure data reliability affects the resolution; however, resolution improves when it is supplemented with other petrophysical information.
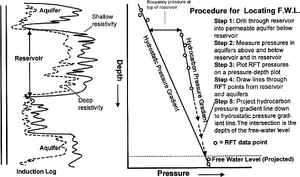
Procedure: using RFT data[edit]
An easy method for determining free-water level (FWL) is projecting RFT pressure data downward from a reservoir to the aquifer. The figure below illustrates the procedure.
Procedure using a single measurement[edit]
The table below outlines the procedure for determining the free-water level using a single pressure buildup point in the reservoir.
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Determine buoyancy pressure (Pb ) at the depth of the measured pressure (Pm ) from the measured pressure:
|
| 2 | Determine buoyancy pressure gradient (Pbg ):
|
| 3 | Calculate downdip length of hydrocarbon column (h):
|
As an example, let's determine the downdip length of a 30°API oil column with the following givens:
- Pm = pressure::3555 psi at depth::7611 ft
- Phydrostatic = 3525 psi
- Phydrostatic pressure gradient = 0.465 psi/ft
- Phydrocarbon pressure gradient = 0.38 psi/ft
Answer (tied back to steps above):
Therefore, the free-water level is at depth::8167 ft.
See also[edit]
- Static hydrocarbon pressure gradients
- Estimating static oil pressure gradients
- Estimating static gas pressure gradients
- Plotting the hydrocarbon pressure gradient