Difference between revisions of "Types of diagenetic traps"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
FWhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
FWhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
* Bottom seal generated below oil-water contacts by [[Postaccumulation cementation|late cementation]] | * Bottom seal generated below oil-water contacts by [[Postaccumulation cementation|late cementation]] | ||
* Primary [[porosity]] preserved due to selective [[Reservoir quality#Cementation|cementation]] and/or early hydrocarbon emplacement | * Primary [[porosity]] preserved due to selective [[Reservoir quality#Cementation|cementation]] and/or early hydrocarbon emplacement | ||
| − | * Secondary porosity created by cement and/or matrix dissolution | + | * [[Secondary porosity]] created by cement and/or matrix dissolution |
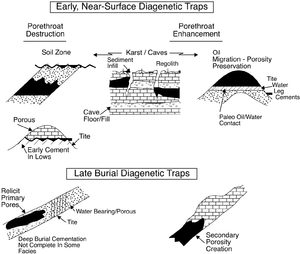
[[:file:exploring-for-stratigraphic-traps_fig21-40.png|Figure 1]] shows cross sections of diagenetic trap types. | [[:file:exploring-for-stratigraphic-traps_fig21-40.png|Figure 1]] shows cross sections of diagenetic trap types. | ||
Revision as of 15:47, 1 May 2014
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps |
| Chapter | Exploring for stratigraphic traps |
| Author | John C. Dolson, Mike S. Bahorich, Rick C. Tobin, Edward A. Beaumont, Louis J. Terlikoski, Michael L. Hendricks |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
Diagenetic traps are created by pore throat modifications of primary facies. They can also be created by changes in fluid type within the pore system.
Categories
Diagenetic traps occur in two basic categories: early or near-surface traps and late-burial traps.
Early or near-surface diagenetic traps are created by the following:
- Reservoir destroyed by paleosols, meteoric cementation, karsting, cave development, and/or sediment infill
- Reservoir enhanced by paleo-groundwater movement and/or karsting
Late burial diagenetic traps are created by the following:
- Bottom seal generated below oil-water contacts by late cementation
- Primary porosity preserved due to selective cementation and/or early hydrocarbon emplacement
- Secondary porosity created by cement and/or matrix dissolution
Figure 1 shows cross sections of diagenetic trap types.
See also
- Diagenetic modifications of stratigraphic traps
- Criteria for recognizing diagenetic traps
- Petrological information about diagenesis
- [[Diagenetic trap regime]