Basin-centered gas systems: global distribution
| Basin-centered gas systems | |

| |
| Series | AAPG Bulletin, November 2002 |
|---|---|
| Author | Ben E. Law |
| Link | Web page |
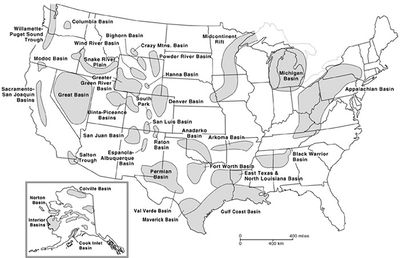
The global distribution of basin-centered gas accumulations (BCGAs) is poorly known, and knowledge of the stratigraphic distribution of BCGAs is incomplete. Even in North America, where most of the exploration activity for BCGAs has occurred, the geographic distribution is not well known. Figure 1 shows the locations of known and suspected BCGAs in the United States. A tabulation of these areas, as well as areas outside North America, is shown in Table 1. The geographic distribution of BCGAs is probably best known in the Rocky Mountain region, where a considerable amount of research has occurred.
Worldwide, there are only a few references available alluding to the presence of BCGAs (Table 1). Many more areas undoubtedly contain BCGAs, but because of the poor understanding of the concepts of BCGSs in countries outside North America, the global distribution of BCGAs is poorly known. For example, in North America, many Rocky Mountain basins contain direct BCGAs. By analogy with Rocky Mountain basins, it is likely that many of the Andean foreland basins of South America also contain BCGAs. Several of the basins in the Middle East and North Africa probably contain indirect BCGAs similar to those in Jordan and Algeria.
| Area | Level of certainty | Age | Type of system | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
NORTH AMERICA
| ||||
| Colville basin, Alaska | High | Cretaceous | Direct ? | Popov et al.[1] |
| Central Alaska basins | Low/Moderate | ? | ? | Popov et al.[1] |
| Cook Inlet, Alaska | Low | pre-Tertiary | ? | Popov et al.[1] |
| Norton Basin, Alaska | High | Eocene/Paleocene | Direct | Smith[2] |
| Alberta basin, Canada | High | Cretaceous | Direct | Masters[3] [4] |
| Charlotte-Georgia Basin, Canada | Low/Moderate | Tertiary/Cretaceous | Direct ? | |
| Willamette-Puget Sound Trough, Washington and Oregon | Moderate/High | Tertiary | Direct ? | Law,[5] Popov et al.[1] |
| Columbia basin, Washington | High | Tertiary | Direct | Law et al.,[6] Law[5] |
| Modoc Plateau, California | Low/Moderate | Cretaceous | Direct ? | Popov et al.[1] |
| Sacramento/San Joaquin basins, California | Low/Moderate | Cretaceous | ? | Popov et al.[1] |
| Great Basin, Nevada | Low | Tertiary ? | ? | Popov et al.[1] |
| Snake River Plain, Idaho | Low/Moderate | Tertiary ? | ? | Popov et al.[1] |
| Big Horn basin, Wyoming | High | Lower Tertiary/Cretaceous | Direct | Johnson et al.[7] |
| Wind River basn, Wyoming | High | Cretaceous | Direct | Johnson et al.[8] |
| Greater Green River basin, Wyoming | High | Lower Tertiary/Cretaceous | Direct | Law et al.,[9] Law et al.,[10] McPeek,[11] Law,[12] Law et al.[13] |
| Hanna basin, Wyoming | High | Cretaceous | Direct | Popov et al.,[1] Wilson et al.[14] |
| Powder River basin, Wyoming | High | Cretaceous | ? | Surdam et al.,[15] Maucione et al.[16] |
| Wasatch Plateau, Utah | Moderate/High | Cretaceous | Direct | Popov et al.[1] |
| Uinta basin, Utah | High | Lower Tertiary/Cretaceous | Direct | Fouch et al.,[17] Fouch and Schmoker,[18] Popov et al.[1] |
| Piceance basin, Colorado | High | Cretaceous | Direct | Johnson et al.,[19] Spencer,[20] Spencer[21] |
| South Park basin, Colorado | Moderate/High | Cretaceous | Direct/Indirect | Popov et al.[1] |
| Raton basin, New Mexico and Colorado | High | Tertiary/Cretaceous | Direct/Indirect | Johnson and Finn,[22] Popov et al.[1] |
| Denver basin, Colorado | High | Cretaceous | Direct/Indirect | Higley et al.,[23] Popov et al.[1] |
| San Juan basin, New Mexico and Colorado | High | Cretaceous | Direct | Silver,[24] Masters,[3] Huffman[25] |
| Permian basin, New Mexico | High | Permian | Indirect/Direct | Broadhead,[26] Popov et al.[1] |
| Albuquerque basin, New Mexico | Moderate/High | Cretaceous | Direct | Johnson et al.[27] Popov et al.[1] |
| Anadarko basin, Oklahoma | High | Pennsylvanian | Indirect | Al-Shaieb et al.,[28] Popov et al.[1] |
| Midcontinent Rift, Minnesota and Iowa | Low/Moderate | Precambrian | Indirect/Direct | Popov et al.[1] |
| Arkoma basin, Arkansas and Oklahoma | High | Pennsylvanian | Direct | Meckel et al.,[29] Popov et al.[1] |
| Gulf Coast, United States | High | Cretaceous | Indirect | Popov et al.[1] |
| East Texas basin, Texas | High | Jurassic | Indirect ? | Montgomery and Karlewiz,[30] Emme and Stancil[31] |
| Black Warrior basin, Alabama and Mississippi | Moderate/High | Pennsylvanian | Direct | Popov et al.[1] |
| Michigan basin, Michigan | Low/Moderate | Ordovician | ? | Popov et al.[1] |
| Appalachian basin, eastern United States | High | Silurian/Devonian | Indirect | Davis,[32] Law and Spencer,[33] Law and Spencer,[34] Popov et al.,[1] Ryder and Zagorski[35] |
SOUTH AMERICA
| ||||
| Chaco basin, Bolivia | Moderate | Devonian | ? | Williams et al.[36] |
| Neuquen basin, Argentina | High | ? | ? | Fernandez-Sevesco and Surdam[37] |
EUROPE
| ||||
| Timan-Pechora basin, Russa | High | Permian | Direct | Law et al.[38] |
| Dnieper-Donets basin, Ukraine | High | Carboniferous | Direct | Law et al.[39] |
| West Netherlands basin, Netherlands | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Vlieland basin, Netherlands | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Polish basin, Poland | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Upper Silesian basin, Poland | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Bekes basin, Hungary | Moderate/High | Miocene | ? | Spencer et al.[40] |
| German basin, Germany | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Ruhr basin, Germany | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Thuringian basin, Germany | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Subhercynian basin, Germany | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Lower Saxony basin, Germany | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Saar-Nahe basin, Germany and France | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Rhine graben, Germany and France | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Nord-pas-de-Calais basin, France | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Lorraine basin, France | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Bresse basin, France | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Southeast basin, France | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Vienna basin, Austria and Slovakia | Indeterminate | ? | ? | |
| Alpine Foreland basin, Switzerland | High | Permian/Carboniferous | Direct | Schegg et al.[41] |
ASIA-PACIFIC
| ||||
| Sichuan basin, China | High | Permian/Triassic | Direct ? | Da-jun and Yun-ho,[42] Ryder et al.[43] |
| Ordos Basin, China | High | Permian | ? | |
| Jungar basin, China | High | Permian | ? | Zha et al.[44] |
| Taranaki Basin, New Zealand | High | Eocene | Direct | |
| Gippsland Basin, Australia | Moderate | Lower Tertiary/Cretaceous | Direct | Stainforth[45] |
| Barrow Subbasin, Australia | High | Jurassic | ? | He and Middleton[46] |
| Perth basin (onshore), Australia | Moderate | Jurassic | ? | Crostella[47] |
| Carnarvon Basin, Australia | Low/Moderate | Permian | ? | Crostella[48] |
| Khorat Plateau basin, Thailand-Laos | Low | Triassic/Jurassic | ? | Smith and Stokes[49] |
SOUTH ASIA
| ||||
| Vendian basin, India | Low/Moderate | Precambrian | ? | |
| Suliaman range foreland, Pakistan | Low | Cretaceous | Direct ? | |
MIDDLE EAST
| ||||
| Risha area, Jordan | High | Ordovician | Indirect | Ahlbrandt et al.[50] |
AFRICA
| ||||
| Ahnet basin, Algeria | High | Cambrian/Ordovician | Indirect | |
| Benue trough, Nigeria | Moderate/High | Cretaceous | Direct | Obaje and Abaa[51] |
The stratigraphic distribution of BCGAs extends from the Cambrian through the Eocene (Table 1). However, there appear to be some differences in the stratigraphic distribution of direct and indirect BCGAs. For example, the preponderance of direct BCGAs occur in Cretaceous through Eocene rocks (Table 1), whereas indirect BCGAs more commonly occur in pre-Cretaceous rocks. Although some of the apparent difference in stratigraphic distribution may be attributable to the disproportionate number of studies in Cretaceous and younger rocks compared to numbers of studies in pre-Cretaceous rocks, the question of seal integrity in direct systems arises. As previously discussed, the effective life of capillary pressure seals in direct systems is not known; therefore, because of the perceptions of a leaky seal in direct systems, the occurrence of direct systems in pre-Cretaceous rocks may be less common than in Cretaceous and younger rocks. Some examples, however, of pre-Cretaceous direct BCGAs include Permian rocks in the Timan-Pechora basin, Russia (Law et al., 1996), and the Sichuan basin, China (Da-jun and Yun-ho, 1994); Pennsylvanian rocks in the Arkoma basin (Meckel et al., 1992); and Carboniferous rocks in the Dnieper-Donets basin, Ukraine (Law et al., 1998b) (Table 1).
Indirect BCGAs occur in rocks ranging from Cambrian through Cretaceous. Examples include Cambrian and Ordovician reservoirs in the Ahnet basin of Algeria, Ordovician reservoirs in Jordan (Ahlbrandt et al., 1997), Lower Silurian reservoirs in the Appalachian basin (Davis, 1984; Law and Dickinson, 1985; Zagorski, 1988, 1991; Law and Spencer, 1993; Law et al., 1998a; Ryder and Zagorski, forthcoming), and Jurassic sandstone reservoirs in the Bossier Shale (Montgomery and Karlewicz, 2001; Emme and Stancil, 2002) in the United States Gulf Coast (Table 1).
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 1.16 1.17 1.18 1.19 1.20 1.21 1.22 Popov, M. A., V. F. Nuccio, T. S. Dyman, T. A. Gognat, R. C. Johnson, J. W. Schmoker, M. S. Wilson, and C. Bartberger, 2001, Basin-centered gas systems of the U.S.:U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 01-135, Version 1.0, 1 CD-ROM.
- ↑ Smith, J. T., 1994, Petroleum system logic as an exploration tool in a frontier setting, in L. B. Magoon and W. G. Dow, eds., The petroleum system-from source to trap: AAPG Memoir 60, p. 25-49.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Masters, J. A., 1979, Deep basin gas trap, western Canada: AAPG Bulletin, v. 63, p. 152-181.
- ↑ Masters, J. A., ed., 1984, Elmworth-case study of a deep basin gas field: AAPG Memoir 38, 316 p.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Law, B. E., 1996, Southwestern Wyoming province (037), in D. L. Gautier, G. L. Dolton, K. I. Takahashi, and K. L. Varnes, eds., 1995 national assessment of United States oil and gas resources-results, methodology, and supporting data: U.S. Geological Survey Digital Data Series DDS-30, Release 2, 1 CD-ROM.
- ↑ Law, B. E., M. E. Tennyson, and S. Y. Johnson 1994, Basin-centered gas accumulations in the Pacific Northwest-a potentially large source of energy (abs.): AAPG Annual Meeting Program, v. 3, p. 194.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedJohnsonetal_1999 - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedJohnsonetal_1996 - ↑ Law, B. E., C. W. Spencer, and N. H. Bostic, 1979, Preliminary results of organic maturation, temperature, and pressure studies in the Pacific Creek area, Sublette County, Wyoming, in 5th Department of Energy symposium on enhanced oil and gas recovery and improved drilling methods, v. 3-oil and gas recovery: Tulsa, Oklahoma, Petroleum Publishing, p. K-2/1-K-2/13.
- ↑ Law, B. E., C. W. Spencer, and N. H. Bostick, 1980, Evaluation of organic maturation, subsurface temperature, and pressure with regard to gas generation in low-permeability Upper Cretaceous and lower Tertiary strata in the Pacific Creek area, Sublette County, Wyoming: Mountain Geologist, v. 17, no. 2, p. 23-35.
- ↑ McPeek, L. A., 1981, Eastern Green River basin-a developing giant gas supply from deep, overpressured Upper Cretaceous sandstones: AAPG Bulletin, v. 65, p. 1078-1098.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedLaw_1984 - ↑ Law, B. E., C. W. Spencer, R. R. Charpentier, R. A. Crovelli, R. F. Mast, G. L. Dolton, and C. J. Wandrey, 1989, Estimates of gas resources in overpressured low-permeability Cretaceous and Tertiary sandstone reservoirs, Greater Green River basin, Wyoming, Colorado, and Utah: 40th Annual Field Conference, Wyoming Geological Association Guidebook, p. 39-61.
- ↑ Wilson, M. S., T. S. Dyman, and V. F. Nuccio, 2001, Potential for deep basin-centered gas accumulations in Hanna basin, Wyoming: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2184-A, 12 p.
- ↑ Surdam, R. C., Z. S. Jiao, and R. S. Martinsen, 1994, The regional pressure regime in Cretaceous sandstones and shales in the Powder River basin, in P. J. Ortoleva, ed., Basin compartments and seals: AAPG Memoir 61, p. 213-233.
- ↑ Maucion, D., V. Serebryakov, P. Valasek, Y. Wang, and S. Smithson, 1994, A sonic log study of abnormally pressured zones in the Powder River basin of Wyoming, in P. J. Ortoleva, ed., Basin compartments and seals: AAPG Memoir 61, p. 333-348.
- ↑ Fouch, T. D., V. F. Nuccio, J. C. Osmond, L. MacMillan, W. B. Cachion, and C. J. Wandrey, 1992, Oil and gas in uppermost Cretaceous and Tertiary rock, Uinta basin, Utah, in T. D. Fouch, V. F. Nuccio, and T. C. Chidsey Jr., eds., Hydrocarbon and mineral resources of the Uinta basin, Utah and Colorado: Utah Geological Association Guidebook 20, p. 9-47.
- ↑ Fouch, T. D., and J. W. Schmoker, 1996, Tight gas plays of the Uinta basin, in D. L. Gautier, G. L. Dolton, K. I. Takahashi, and K. L. Varnes, eds, 1995 national assessment of United States oil and gas resources-results, methodology, and supporting data: U.S. Geological Survey Digital Data Series DDS-30, Release 2, 1 CD-ROM.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedJohnsonetal_1987 - ↑ Spencer, C. W., 1987, Hydrocarbon generation as a mechanism for overpressuring in Rocky Mountain region: AAPG Bulletin, v. 71, p. 368-388.
- ↑ Spencer, C. W., 1989, Review of characteristics of low-permeability gas reservoirs in western United States: AAPG Bulletin, v. 73, p. 613-629.
- ↑ Johnson, R. C., and T. M. Finn, 2001, Potential for basin-centered gas accumulation in the Raton basin, Colorado and New Mexico: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2184-B, 14 p.
- ↑ Higley, D. K., D. L. Gautier, and M. J. Pawlewicz, 1992, Influence of regional head flow variation on thermal maturity of the Lower Cretaceous Muddy ("J") Sandstone, Denver basin, Colorado, in The petroleum system-status of research and methods, 1992: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2007, p. 66-69.
- ↑ Silver, C., 1950, The occurrence of gas in the Cretaceous rocks of the San Juan basin, New Mexico and Colorado: New Mexico Geological Society, First Field Conference, San Juan basin, p. 109-123.
- ↑ Huffman, A. C., 1996, San Juan basin province, in D. L. Gautier, G. L. Dolton, K. I. Takahashi, and K. L. Varnes, eds, 1995 national assessment of United States oil and gas resources-results, methodology, and supporting data: U.S. Geological Survey Digital Data Series DDS-30, Release 2, 1 CD-ROM.
- ↑ Broadhead, R. F., 1984, Geology of gas production from tight Abo red beds, east central New Mexico: Oil & Gas Journal, v. 82, no. 24, p. 147-158.
- ↑ Johnson, R. C., T. M. Finn, and V. F. Nuccio, 2001, Potential for basin-centered gas accumulation in the Albuquerque basin, New Mexico: U.S. Geological Survey Bulletin 2184-C, 21 p.
- ↑ Al-Shaieb, Z., J. Puckette, A. Abdalla, and P. B. Ely, 1994, Megacompartment complex in the Anadarko basin: A completely sealed overpressured phenomenon, in P. J. Ortoleva, ed., Basin compartments and seals: AAPG Memoir 61, p. 55-62.
- ↑ Meckel, L. D., D. G. Smith, and L. A. Wells, 1992, Ouachita foredeep basins: Regional paleogeography and habitat of hydrocarbons, in R. W. Macqueen and D. A. Leckie, eds., Foreland basins and fold belts: AAPG Memoir 55, p. 427-444.
- ↑ Montgomery, S. L., and R. Karlewicz, 2001, Bossier play has room to grow: Oil & Gas Journal, v. 99, no. 5, p. 36-42.
- ↑ Emme, J., and B. Stancil, 2002, Anadarko's Bossier gas play-a sleeping giant in a mature basin (abs.): AAPG Annual Meeting Program, v. 11, p. A50.
- ↑ Davis, T. B., 1984, Subsurface pressure profiles in gas saturated basins, in J. A. Masters, ed., Elmworth-case study of a deep basin gas field: AAPG Memoir 38, p. 189-203.
- ↑ Law, B. E., and C. W. Spencer, 1993, Gas in tight reservoirs-an emerging source of energy, in D. G. Howell, ed., The future of energy gases: U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper 1570, p. 233-252.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedLawandspencer_1998 - ↑ Ryder, R. T., and W. A. Zagorski, 2003, Nature, origin, and production characteristics of the Lower Silurian regional oil and gas accumulation, central Appalachian basin, United States: AAPG Bulletin, v. 87, no. 5, p. 847-872.
- ↑ Williams, K. E., B. J. Radovich, and J. W. Brett, 1995, Exploration for deep gas in the Devonian Chaco basin of southern Bolivia: Sequence stratigraphy, prediction, and well results (abs.): AAPG Annual Convention, Abstracts with Program, v. 4, p. A104.
- ↑ Fernandez-Sevesco, F., and R. C. Surdam, 1997, A new exploration approach in the search for anomalously pressured hydrocarbon accumulations in the Neuquen Basin, Argentina (abs.): AAPG International Conference and Exhibition Program, p. A16.
- ↑ Law, B. E., V. I. Bogatsky, S. . Danilevsky, L. V. Galkina, G. F. Ulmishek, and C. W. Spencer, 1996, Basin-centered gas accumulations in the Timan-Pechora basin, Russia (abs.): AAPG Annual Convention Program, v. 5, p. A81.
- ↑ Law, B. E., G. F. Ulmishek, B. P. Kabyshev, N. T. Pashova, and V. A. Krivosheya, 1998, Basin-centered gas evaluated in Dnieper-Donets basin, Donbas foldbelt, Ukraine: Oil & Gas Journal, v. 100, no. 30, p. 74-78.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedSpenceretal_1994 - ↑ Schegge, R., W. Leu, and E. Greber, 1997, New exploration concepts spark Swiss gas, oil prospects: Oil & Gas Journal, v. 95, no. 39, p. 102-106.
- ↑ Da-jun, P., and L. Yun-ho, 1994, Genetic mechanism of abnormal pressure, pressure seals, and natural gas accumulation in carbonate reservoirs, Sichuan basin: Proceedings of the AAPG Research Conference Abnormal Pressures in Hydrocarbon Environments, unpaginated.
- ↑ Ryder, R. T., D. D. Rice, Z. Sun, Y. Zhanz, Y. Qui, and Z. Guo, 1994, Petroleum geology of the Sichuan basin China-report on U.S. Geological Survey and Chinese Ministry of Geology and Mineral Resources, field investigation and meeting, October 1991: U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 94-426, 67 p.
- ↑ Zha, M., W. Zhang, and Q. Jiangxiu, 1999, Overpressured compartments in Junggar basin, northwest of China: Mechanisms and hydrocarbon distribution (abs.): AAPG Annual Convention, Program with Abstracts, v. 8, p. A158-159.
- ↑ Stainforth, J.G., 1984, Gippsland hydrocarbons-a perspective from the basin edge: Australian Petroleum Exploration Association Journal, v. 24, p. 91-100.
- ↑ He, S., and M. Middleton, 2002, Pressure seal and modeling of the Jurassic overpressure in the Barrow Sub-basin, northwest shelf of Australia (abs.): AAPG Annual Meeting Program, v. 11, p. A74.
- ↑ Crostella, A., 1995, An evaluation of the hydrocarbon potential of the onshore Northern Perth basin, western Australia: Geological Survey of Western Australia Report 43, 67 p.
- ↑ Crostella, A., 1995, Structural evolution and hydrocarbon potential of the Merlinliegh and Byro sub-basins, Canarvon basin, western Australia: Geological Survey of Western Australia Report 45, 35 p.
- ↑ Smith, P. F. L., and R. B. Stokes, 1997, Geology and petroleum potential of the Khorat Plateau Basin in the Vientiane area of Lao P.D.R.: Journal of Petroleum Geology, v. 20, p. 27-50.
- ↑ Ahlbrandt, T. S., O. A. Okasheh, and M. Lewan, 1997, A Middle East basin center hydrocarbon accumulation in Paleozoic rocks, eastern Jordan, western Iraq, and surrounding areas (abs.): AAPG International Conference and Exhibition, p. A1-A2.
- ↑ Obaje, N. G., and S. I. Abaa, 1996, Potential for col-derived gaseous hydrocarbons in the middle Benue Trough of Nigeria: Journal of Petroleum Geology, v. 19, p. 77-94.
See also
- Basin-centered gas
- Basin-centered gas systems: historical development and classification
- Basin-centered gas systems
- Basin-centered gas systems: elements and processes
- Basin-centered gas systems: examples
- Basin-centered gas systems: gas resources
- Basin-centered gas systems: development
- Basin-centered gas systems: evaluation and exploration strategies
- Tight gas reservoirs: evaluation