Difference between revisions of "Free water level determination using pressure"
Cwhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
Cwhitehurst (talk | contribs) m (added Category:Treatise Handbook 3 using HotCat) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
# Determine buoyancy pressure gradient (''P''<sub>bg</sub> ): | # Determine buoyancy pressure gradient (''P''<sub>bg</sub> ): | ||
#*:<math>P_{\rm bg} = P_{\rm hydrostatic\ pressure\ gradient} - P_{\rm hydrocarbon\ pressure\ gradient}</math> | #*:<math>P_{\rm bg} = P_{\rm hydrostatic\ pressure\ gradient} - P_{\rm hydrocarbon\ pressure\ gradient}</math> | ||
| − | # Calculate downdip length of hydrocarbon column (''h''): | + | # Calculate downdip length of [[hydrocarbon column]] (''h''): |
#*:<math>h = \frac{P_{\rm b}}{P_{\rm bg}}</math> | #*:<math>h = \frac{P_{\rm b}}{P_{\rm bg}}</math> | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
[[Category:Critical elements of the petroleum system]] | [[Category:Critical elements of the petroleum system]] | ||
[[Category:Formation fluid pressure and its application]] | [[Category:Formation fluid pressure and its application]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Treatise Handbook 3]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:54, 17 February 2022
The free water level occurs where buoyancy pressure is zero in the reservoir-aquifer system. It defines the downdip limits of an accumulation. Pressure data reliability affects the resolution; however, resolution improves when it is supplemented with other petrophysical information.
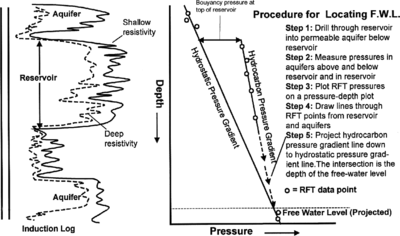
Procedure: using repeat formation tester (RFT) data[edit]
An easy method for determining free water level (FWL) is projecting RFT pressure data downward from a reservoir to the aquifer. Figure 1 illustrates the procedure.
Procedure using a single measurement[edit]
The list below outlines the procedure for determining the free water level using a single pressure buildup point in the reservoir.
- Determine buoyancy pressure (Pb ) at the depth of the measured pressure (Pm ) from the measured pressure:
- Determine buoyancy pressure gradient (Pbg ):
- Calculate downdip length of hydrocarbon column (h):
As an example, let's determine the downdip length of a 30°API oil column with the following givens:
- Pm = pressure::3555 psi at depth::7611 ft
- Phydrostatic = 3525 psi
- Phydrostatic pressure gradient = 0.465 psi/ft
- Phydrocarbon pressure gradient = 0.38 psi/ft
Answer (tied back to steps above):
Therefore, the free water level is at depth::8167 ft.
See also[edit]
- Static hydrocarbon pressure gradients
- Estimating static oil pressure gradients
- Estimating static gas pressure gradients
- Plotting the hydrocarbon pressure gradient