Difference between revisions of "Sandstone diagenetic processes"
Cwhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
Cwhitehurst (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
| part = Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps | | part = Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps | ||
| chapter = Predicting reservoir system quality and performance | | chapter = Predicting reservoir system quality and performance | ||
| − | | frompg = 9- | + | | frompg = 9-76 |
| − | | topg = 9- | + | | topg = 9-77 |
| author = Dan J. Hartmann, Edward A. Beaumont | | author = Dan J. Hartmann, Edward A. Beaumont | ||
| link = http://archives.datapages.com/data/specpubs/beaumont/ch09/ch09.htm | | link = http://archives.datapages.com/data/specpubs/beaumont/ch09/ch09.htm | ||
Revision as of 20:02, 4 March 2015
| Exploring for Oil and Gas Traps | |

| |
| Series | Treatise in Petroleum Geology |
|---|---|
| Part | Predicting the occurrence of oil and gas traps |
| Chapter | Predicting reservoir system quality and performance |
| Author | Dan J. Hartmann, Edward A. Beaumont |
| Link | Web page |
| Store | AAPG Store |
Diagenesis alters the original pore type and geometry of a sandstone and therefore controls its ultimate porosity and permeability. Early diagenetic patterns correlate with environment of deposition and sediment composition. Later diagenetic patterns cross facies boundaries and depend on regional fluid migration patterns (Stonecipher and May, 1992). Effectively predicting sandstone quality depends on predicting diagenetic history as a product of depositional environments, sediment composition, and fluid migration patterns.
Diagenetic processes
Sandstone diagenesis occurs by three processes:
- Cementation
- Dissolution (leaching)
- Compaction
Cementation destroys pore space; grain leaching creates it. Compaction decreases porosity through grain rearrangement, plastic deformation, pressure solution, and fracturing.
Diagenetic zones
Surdam et al.[1] define diagenetic zones by subsurface temperatures. Depending on geothermal gradient, depths to these zones can vary. The table below summarizes major diagenetic processes and their impact on pore geometry.
| Zone | Temperature | Major diagenetic processes | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Preserves or enhances porosity | Destroys porosity | ||
| Shallow | <80°C or 176°F (<5,00 to 10,00 ft) |
|
|
| Intermediate | 80-140°C or 176–284°F |
|
|
| Deep | > 140°C or 284°F |
|
|
Effect of temperature
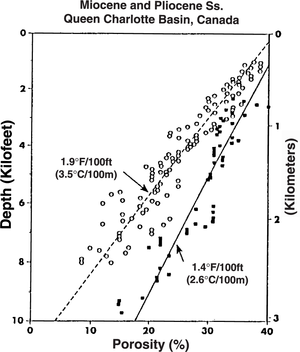
Depending on geothermal gradient, the effect of temperature on diagenesis can be significant. Many diagenetic reaction rates double with each temperature::10°C increase (1000 times greater with each temperature::100°C).[2] Increasing temperatures increase the solubility of many different minerals, so pore waters become saturated with more ionic species. Either (1) porosity–depth plots of sandstones of the target sandstone that are near the prospect area or (2) computer models that incorporate geothermal gradient are probably best for porosity predictions.
Figure 1 is a porosity–depth plot for sandstones from two wells with different geothermal gradients. The well with the greater geothermal gradient has correspondingly lower porosities than the well with lower geothermal gradient. At a depth of depth::7000 ft, there is a 10% porosity difference in the trend lines.
Effect of pressure
The main effect of pressure is compaction. The process of porosity loss with depth of burial is slowed by overpressures. Basing his findings mainly on North Sea sandstones, Scherer[3] notes sandstones retain approximately 2% porosity for every pressure::1000 psi of overpressure during compaction. He cautions this figure must be used carefully because the influence of pressure on porosity depends on the stage of compaction at which the overpressure developed.
Effect of age
In general, sandstones lose porosity with age. In other words, porosity loss in sandstone is a function of time. According to Scherer,[3] a Tertiary sandstone with a Trask sorting coefficient of 1.5, a quartz content of 75%, and a burial depth of depth::3000 m probably has an average porosity of approximately 26%. A Paleozoic sandstone with the same sorting, quartz content, and burial depth probably has an average porosity of approximately 13%.
See also
- Predicting sandstone porosity and permeability
- Effect of composition and texture on sandstone diagenesis
- Hydrology and sandstone diagenesis
- Influence of depositional environment on sandstone diagenesis
- Predicting sandstone reservoir porosity
- Predicting sandstone permeability from texture
- Estimating sandstone permeability from cuttings
References
- ↑ Surdam, R., C., Dunn, T., L., MacGowan, D., B., Heasler, H., P., 1989, Conceptual models for the prediction of porosity evolution with an example from the Frontier Sandstone, Bighorn basin, Wyoming, in Coalson, E., B., Kaplan, S., S., Keighin, C., W., Oglesby, L., A., Robinson, J., W., eds., Sandstone Reservoirs: Rocky Mountain Association of Geologists, p. 7–21.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wilson, M., D., 1994a, Non-compositional controls on diagenetic processes, in Wilson, M., D., ed., Reservoir quality Assessment and Prediction in Clastic Rocks: SEPM Short Course 30, p. 183–208. Discusses the effect that variables such as temperature and pressure have on diagenesis of sandstones. A good reference for predicting sandstone reservoir system quality.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Scherer, M., 1987, Parameters influencing porosity in sandstones: a model for sandstone porosity prediction: AAPG Bulletin, vol. 71, no. 5, p. 485–491.