Fluid contacts
Positions of initial fluid contacts are critical for field reserve estimates and for field development. Typically, the position of fluid contacts are first determined within control wells and then extrapolated to other parts of the field.
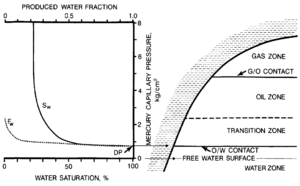
Definitions of fluid contacts are based on comparison to capillary pressure curves (Figure 1) . The free water surface is the highest elevation at which the pressure of the hydrocarbon phase is the same as that of water. The hydrocarbon-water (oil-water or gas-water) contact is the lowest elevation at which mobile hydrocarbons occur. The transition zone is the elevation range in which water is coproduced with hydrocarbons. The gas-oil contact is the elevation above which gas is the produced hydrocarbon phase.
Methods for determining fluid contacts[edit]
Methods for determining initial fluid contacts are listed in Table 1 and are discussed by Bradley.[1] These include fluid sampling methods, saturation estimation from wireline logs, estimation from conventional and sidewall cores, and pressure methods. Once initial fluid contact elevations in control wells are determined, the contacts in other parts of the reservoir can be estimated. Initial fluid contacts within most reservoirs having a high degree of continuity are almost horizontal, so the reservoir fluid contact elevations are those of the control wells.
| Method | Description | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fluid sampling: production tests drill stem tests RFT tests | Directly determines fluid contacts by measuring recovered fluids | Direct measure of fluid contact | Rarely closely spaced, so contacts must be interpolated |
| Problems with filtrate recovery on DST and RFT | |||
| Coning, degassing, etc. may lead to anomalous recoveries | |||
| Saturation determination: well logs | Estimates fluid contacts from changes in fluid saturations or mobility with depth | Low cost Accurate in simple lithologies | Saturation must be calibrated to production |
| Rapid High resolution | Unreliable in complex lithologies or low resistivity sands | ||
| Saturation determination: core analyses | Estimates fluid contacts from changes in fluid saturation with depth | Saturation estimates for complex lithologies | Saturation measurements may not be accurate |
| Saturation can be related to petro-physical properties | Usually not continuously cored, so saturation profile is not as complete | ||
| Pressure profiles: RFT tests | Estimates free-water surface from inflections in pressure versus depth curve | Little affected by lithology or coning | Imprecise; data usually require correction |
| Only useful for thick hydrocarbon columns | |||
| Most reliable for gas contacts Requires many pressure measurements for profile Requires accurate pressures | |||
| Pressure profiles: reservoir tests production tests drill stem tests | Estimates free water surface from pressures and fluid density measurements | Makes use of widely available pressure data | Imprecise; data usually require significant correction Only useful for thick hydrocarbon columns |
| Most reliable for gas contacts Requires pressure tests from both fluid zones and assumed or measured fluid densities to estimate contact Requires accurate pressures |
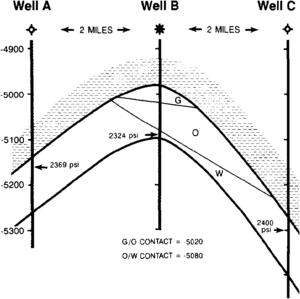
Some reservoirs have irregular or tilted fluid contacts (Figure 2). Reasons for differences in contact elevation in different control wells must first be determined to properly extrapolate nonhorizontal fluid contacts to untested parts of a reservoir. Excluding interpretation or mechanical problems, the most common reasons for tilted fluid contacts are the following:
- Hydrodynamic gradients
- Reservoir heterogeneity (see Geological heterogeneities)
- Semipermeable barriers
Situations can usually be distinguished because they are associated with different geological settings and result in different fluid contact characteristics (Table 2).
| Type | Cause | Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrodynamic tilt | Moving water at the reservoir interval | Presence of hydrodynamic conditions Fluid contact dip angles and directions are constant over the field despite facies changes. Oil-water contact has a steeper dip than the gas contacts, but all contacts dip in the same direction Significant dip to gas contacts are rare |
| Reservoir heterogeneity | Differences of hydrocarbon saturation and hydrocarbon permeability due to capillary effects on different pore systems | Presence of several reservoir lithologies with different capillary properties Fluid contacts at facies changes Oil-water and gas-water contacts affected; gas-oil contact not affected Hydrocarbon and water production may be intercalated |
| Semipermeable barriers | Semipermeable barriers compartmentalize an otherwise homogeneous reservoir | Fluid contacts horizontal, yet at different elevations in different parts of the pool; All types of fluid contacts affected Barriers are documented in locations which might cause observed compartmentalization; Contact changes do not correspond to regional hydrodynamics or changes in capillary properties |
Hydrodynamic gradients[edit]
A common type of nonhorizontal oil-water contact is tilting in response to hydrodynamics, the movement of water in the reservoir interval. Hydrodynamic conditions that affect fluid contacts are usually associated with active meteoric aquifers at relatively shallow depths. Indications of active meteoric flow include low salinity water, high topographic relief, and proximity to recharge areas.
If purely hydrodynamic in origin, the fluid contact tilt can be extrapolated across the field as a flat plane that intersects the contact elevation in a minimum of three control wells. Regional fluid pressure data can be used to extrapolate the fluid contacts from the contacts measured in one or two wells. Only corrected shut-in pressures unaffected by nearby production should be used for this evaluation.
Hydrodynamic potential (h) is usually measured as the elevation to which water would rise in an open borehole, called the Potentiometric elevation. It is calculated from the reservoir pressure by the following relationship:
where
- P = corrected shut-in pressure
- C = pressure gradient constant (0.433 psi/ft or 0.1 kg/cm2/m)
- ρw = specific gravity of water
- Em = pressure measurement
- Er = reference elevation (not subsurface depth)
Potentiometric elevations are mapped and contoured to determine the change in Potentiometric elevation per unit distance, called the Potentiometric gradient. The hydrodynamic tilt of a fluid contact can be estimated from the Potentiometric gradient and fluid densities by the following relationship[2][3]:
and
The Potentiometric gradient is approximately constant along the section at 17 ft/mi. Calculating the contact dip from Equation (2), we have
The fluid contacts are graphically projected away from well B at the calculated dips to determine the contact elevations along the cross section.
Reservoir heterogeneity[edit]
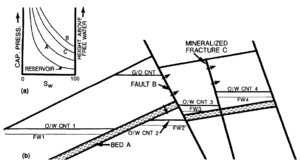
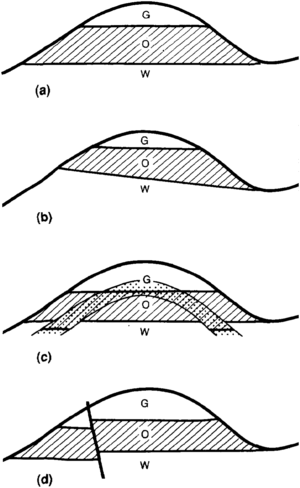
Reservoir rocks may have substantially different pore structures in different parts of a field. These heterogeneities may result in significant variations in hydrocarbon-water contacts, especially in low permeability reservoirs (Figure 4). Where all reservoir facies are very porous, heterogeneity of depositional environments does not significantly affect fluid contact elevation.
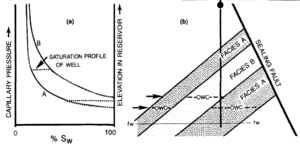
Fluid contact elevations in different control wells can be empirically related to lithofacies at the contact. Where critical lithofacies are not penetrated at the fluid contact, the contact elevation of the lithofacies can be predicted from capillary pressure and relative permeability tests (see “Relative Permeabilities”). The greater the difference in capillary pressure and relative permeability behavior for different lithologies within a reservoir, the greater the potential for fluid contact differences caused by heterogeneity. Because surface tension between oil and gas is usually low in subsurface reservoirs,[4] the effect of reservoir heterogeneity on oil-gas contacts is usually small.
Fluid contacts can be extrapolated from control wells if distribution of different reservoir rock types and their capillary properties can be mapped. In many cases, the distribution of rock types within heterogeneous reservoirs is poorly characterized during initial development, so the largest uncertainty in mapping the fluid contact is the uncertainty in the distribution of the lithofacies. The position of the hydrocarbon-water contact may need to be confirmed by well penetration.
Semipermeable fluid barriers[edit]
Semipermeable barriers can divide a reservoir into compartments with different fluid contacts even if the capillary properties of the reservoir rock are the same on both sides of the barrier. Semipermeable barriers can include faults, mineralized fractures, or semipermeable beds. The resulting pool has horizontal fluid contacts, but the contacts occur at different elevations on different sides of the barrier (Figure 5). The elevation difference between fluid contacts is related to the displacement pressure of the semipermeable barrier.[5] Whereas fault or mineralized fracture compartmentalization is not readily recognized without detailed mapping, semipermeable beds are commonly recognized and the reservoir is separated into different pools corresponding to the different fluid contacts. Once the position of the barrier is mapped and the elevations of the contact on either side are determined from control wells, the fluid contacts can be mapped as horizontal surfaces within each compartment of the pool. Limited communication across semipermeable barriers is possible during production from the pool.
Anomalously thick transition zones[edit]
The transition zones calculated for homogeneous reservoirs may be relatively thin, particularly in coarsegrained reservoirs. However, thick transition zones are observed in many fields due to reservoir heterogeneity. Interbedded lithologies with different capillary behaviors may result in a thick transition zone in which some lithologies produce hydrocarbons and others produce water. Rocks with complex pore networks (such as combined fracture and matrix porosity) may also have a thick transition zone, with different fluid types produced from different pore types. The cause of thick transition zones may be evaluated by combined core examination and capillary pressure tests. Some intervals within transition zones characterized by interbedded lithologies may be brought into low water production by selective perforation.
Upward movement of hydrocarbon-water contacts may leave a zone of residual hydrocarbon saturation below the present transition zone. The hydrocarbons might be interpreted as part of a transition zone from well log or core analysis, leading to an erroneous approximation of fluid contacts or rock properties. The presence of residual hydrocarbon saturation below an oil pool can sometimes be detected by the presence of two inflections in the plot of hydrocarbon saturation against depth, one at the present transition zone and another at the original transition zone.
See also[edit]
- Introduction to geological methods
- Subsurface maps
- Flow units for reservoir characterization
- Effective pay determination
- Evaluating tight gas reservoirs
References[edit]
- ↑ Bradley, H. B., ed., 1987, Petroleum Engineering Handbook: Richardson, TX, Society of Petroleum Engineers.
- ↑ Hubbert, M. K., 1953, Entrapment of petroleum under hydrodynamic conditions: AAPG Bulletin, v. 37, p. 1954–2026.
- ↑ Dahlberg, E. C., 1982, Applied Hydrodynamics in Petroleum Exploration: New York, Springer Verlag, 161 p.
- ↑ Katz et al., 1957, Handbook of Natural Gas Engineering: New York, McGraw-Hill, 802 p.
- ↑ Watts, N. L., 1987, Theoretical aspects of cap-rock and fault seals for single- and two-phase hydrocarbon columns: Marine and Petroleum Geology, v. 4, p. 274–307., 10., 1016/0264-8172(87)90008-0